Home > Press > Battery components can take the heat: Rice University team creates robust 'white graphene' electrolyte and separator for lithium-ion batteries
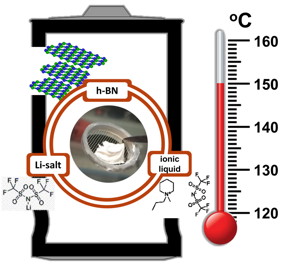 |
| Rice materials scientists produce an electrolyte/separator for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries that withstands very high temperatures over many charge cycles. The key component is hexagonal boron nitride. Credit: Illustration by Hemtej Gullapalli/Rice University |
Abstract:
Rice University materials scientists have introduced a combined electrolyte and separator for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries that supplies energy at usable voltages and in high temperatures.
Battery components can take the heat: Rice University team creates robust 'white graphene' electrolyte and separator for lithium-ion batteries
Houston, TX | Posted on April 11th, 2016An essential part of the nonflammable, toothpaste-like composite is hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), the atom-thin compound often called "white graphene."
The Rice team led by materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan said batteries made with the composite functioned perfectly in temperatures of 150 degrees Celsius (302 degrees Fahrenheit) for more than a month with negligible loss of efficiency. Test batteries consistently operated from room temperature to 150 C, setting one of the widest temperature ranges ever reported for such devices, the researchers said.
"We tested our composite against benchmark electrodes and found that the batteries were stable for more than 600 cycles of charge and discharge at high temperatures," said lead author Marco-Túlio Rodrigues, a Rice graduate student.
The results were reported in Advanced Energy Materials.
Last year members of a Rice and Wayne State University team introduced an electrolyte made primarily of common bentonite clay that operated at 120 C. This year the team validated its hunch that h-BN would serve the purpose even better.
Rodrigues said batteries with the new electrolyte are geared more toward industrial and aerospace applications than cellphones. In particular, oil and gas companies require robust batteries to power sensors on wellheads. "They put a lot of sensors around drill bits, which experience extreme temperatures," he said. "It’s a real challenge to power these devices when they are thousands of feet downhole."
"At present, nonrechargeable batteries are heavily used for the majority of these applications, which pose practical limitations on changing batteries on each discharge and also for disposing their raw materials," said Rice alumnus and co-author Leela Mohana Reddy Arava, now an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Wayne State.
Hexagonal boron nitride is not a conductor and is not known to be an ionic conductor, Rodrigues said. "So we didn't expect it to be any obvious help to battery performance. But we thought a material that is chemically and mechanically resistant, even at very high temperatures, might give some stability to the electrolyte layer."
He said boron nitride is a common component in ceramics for high-temperature applications. "It's fairly inert, so it shouldn't react with any chemicals, it won't expand or contract a lot and the temperature isn't a problem. That made it perfect."
The material eliminates the need for conventional plastic or polymer separators, membranes that keep a battery's electrodes apart to prevent short circuits. "They tend to shrink or melt at high temperatures," said Rice postdoctoral researcher and co-author Hemtej Gullapalli.
Tests went better than the researchers anticipated. Though inert, the mix of h-BN, piperidinium-based ionic liquid and a lithium salt seemed to catalyze a better reaction from all the chemicals around it.
"It took almost two years to confirm that even though the boron nitride, which is a very simple formulation, is not expected to have any chemical reaction, it's giving a positive contribution to the way the battery works," Gullapalli said. "It actually makes the electrolyte more stable in situations when you have high temperature and high voltages combined."
He noted all the electrolyte's components are nonflammable. "It's completely safe. If there's a failure, it's not going to catch fire," he said.
"Our group has been interested in designing energy storage devices with expandable form factors and working conditions," Ajayan said. "We had previously designed paper and paintable battery concepts that change the fundamental way power delivery can be imagined. Similarly, pushing the boundaries of working temperature ranges is very interesting. There is no commercial battery product that works above about 80 C. Our interest is to break this barrier and create stable batteries at twice this temperature limit or more."
Co-authors are Rice graduate student Kaushik Kalaga and Wayne State postdoctoral fellow Ganguli Babu. Ajayan is chair of Rice’s Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering, the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering and a professor of chemistry.
The University of Texas at Austin through the Advanced Energy Consortium supported the project.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to tinyurl.com/AboutRiceUniversity.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Rice University Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Rice University Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








