Home > Press > Crumpling approach enhances photodetectors' light responsivity
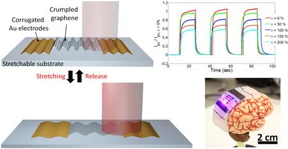 |
| Stretchable photodetector with enhanced, strain-tunable photoresponsivity was created by engineering the 2D graphene material into 3D structures, increasing the graphene’s areal density. Credit: University of Illinois College of Engineering |
Abstract:
Researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated a new approach to modifying the light absorption and stretchability of atomically thin two-dimensional (2D) materials by surface topographic engineering using only mechanical strain. The highly flexible system has future potential for wearable technology and integrated biomedical optical sensing technology when combined with flexible light-emitting diodes.
Crumpling approach enhances photodetectors' light responsivity
Posted on April 7th, 2016"Increasing graphene's low light absorption in visible range is an important prerequisite for its broad potential applications in photonics and sensing," explained SungWoo Nam, an assistant professor of mechanical science and engineering at Illinois. "This is the very first stretchable photodetector based exclusively on graphene with strain-tunable photoresponsivity and wavelength selectivity."
Graphene--an atomically thin layer of hexagonally bonded carbon atoms--has been extensively investigated in advanced photodetectors for its broadband absorption, high carrier mobility, and mechanical flexibility. Due to graphene's low optical absorptivity, graphene photodetector research so far has focused on hybrid systems to increase photoabsorption. However, such hybrid systems require a complicated integration process, and lead to reduced carrier mobility due to the heterogeneous interfaces.
According to Nam, the key element enabling increased absorption and stretchability requires engineering the two-dimensional material into three-dimensional (3D) "crumpled structures," increasing the graphene's areal density. The continuously undulating 3D surface induces an areal density increase to yield higher optical absorption per unit area, thereby improving photoresponsivity. Crumple density, height, and pitch are modulated by applied strain and the crumpling is fully reversible during cyclical stretching and release, introducing a new capability of strain-tunable photoabsorption enhancement and allowing for a highly responsive photodetector based on a single graphene layer.
"We achieved more than an order-of-magnitude enhancement of the optical extinction via the buckled 3D structure, which led to an approximately 400% enhancement in photoresponsivity," stated Pilgyu Kang, and first author of the paper, "Crumpled Graphene Photodetector with Enhanced, Strain-tunable and Wavelength-selective Photoresponsivity," appearing in the journal, Advanced Materials. "The new strain-tunable photoresponsivity resulted in a 100% modulation in photoresponsivity with a 200% applied strain. By integrating colloidal photonic crystal--a strain-tunable optomechanical filter--with the stretchable graphene photodetector, we also demonstrated a unique strain-tunable wavelength selectivity."
"This work demonstrates a robust approach for stretchable and flexible graphene photodetector devices," Nam added. "We are the first to report a stretchable photodetector with stretching capability to 200% of its original length and no limit on detection wavelength. Furthermore, our approach to enhancing photoabsorption by crumpled structures can be applied not only to graphene, but also to other emerging 2D materials."
###
In addition to Nam and Kang, study co-authors include Michael Cai Wang and Peter M. Knapp in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering at Illinois. The optical characterizations and partial device fabrication were carried out in the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory and the Micro and Nano Technology Laboratory at Illinois.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
SungWoo Nam
217-300-0267
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








