Home > Press > Research reveals carbon films can give microchips energy storage capability: International team from Drexel University and Paul Sabatier University reveals versatility of carbon films
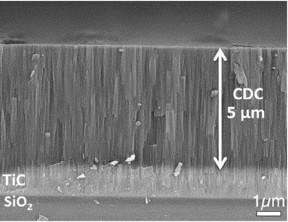 |
| This is the layered structure of the carbon films on silicon chips. CREDIT: A. Demortiere/LRCS |
Abstract:
After more than half a decade of speculation, fabrication, modeling and testing, an international team of researchers led by Drexel University's Dr. Yury Gogotsi and Dr. Patrice Simon, of Paul Sabatier University in Toulouse, France, have confirmed that their process for making carbon films and micro-supercapacitors will allow microchips and their power sources to become one and the same.
Research reveals carbon films can give microchips energy storage capability: International team from Drexel University and Paul Sabatier University reveals versatility of carbon films
Philadelphia, PA | Posted on February 11th, 2016The discovery, which was reported in the Feb. 12 edition of the journal Science, is the culmination of years of collaborative research by the team who initially created the carbide-derived carbon film material for microsupercapacitors and published the concept paper in Science in 2010. Since then, their goal has been to show that it's possible to physically couple the processing center of an electronic device -- the microchip -- with its energy source.
"This has taken us quite some time, but we set a lofty goal of not just making an energy storage device as small as a microchip -- but actually making an energy storage device that is part of the microchip and to do it in a way that is easily integrated into current silicon chip manufacturing processes," said Simon, who led the research under the aegis of the French research network on electrochemical energy storage (RS2E). "With this achievement, the future is now wide open for chip and personal electronics manufacturers."
It confirms a belief that the group has held since the materials were first fabricated -- that these films are versatile enough to be seamlessly integrated into the systems that power silicon-based microchips that run devices from your laptop to your smart watch.
The challenges that the group faced in the development of the material were questions about its compatibility, its mechanical stability and durability for use on flexible substrates. With these answered, it opens up a myriad of possibilities for carbon films to work their way into silicon chips -- including building microscale batteries on a chip.
"The place where most people will eventually notice the impact of this development is in the size of their personal electronic devices, their smart phones, fitbits89 and watches," said Gogotsi, Distinguished University and Trustee Chair Professor in the Department of Materials Science Engineering who directs the A.J. Drexel Nanomaterials Institute in Drexel's College of Engineering. "Even more importantly," Gogotsi adds, "on-chip energy storage is needed to create the Internet of Things - the network of all kinds of physical objects ranging from vehicles and buildings to our clothes embedded with electronics, sensors, and network connectivity, which enables these objects to collect and exchange data. This work is an important step toward that future."
The researchers' method for depositing carbon onto a silicon wafer is consistent with microchip fabrication procedures currently in use, thus easing the challenges of integration of energy storage devices into electronic device architecture. As part of the research, the group showed how it could deposit the carbon films on silicon wafers in a variety of shapes and configurations to create dozens of supercapacitors on a single silicon wafer.
Supercapacitors have been desirable devices to use in microelectronics because they can store a great deal of energy for their size, they can be charged and discharged their energy extremely quickly and their lifespan is nearly limitless. With this discovery, the path is clear for microchip manufacturers to take a big step forward in the way they design their products.
Beyond the energy storage applications, these carbon films offer good prospects for the development of elastic coatings with a low coefficient of friction that can be used in lubricant-free sliding parts, such as dynamic seals. They may also be used in production of membranes for gas filtration, water desalination or purification, because their pore size is in the range of single molecules. The carbon films produced by this method are quite versatile and may find applications in many areas.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Britt Faulstick
215-895-2617
Copyright © Drexel University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








