Home > Press > A clue to generate electric current without energy consumption at room temperature
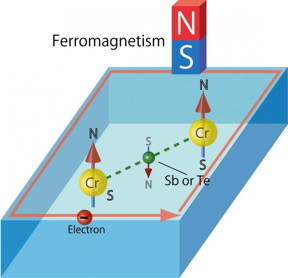 |
| Sb atoms and Te atoms serve as the glue to fix the N-S orientations of Cr atoms in Cr-doped (Sb, Bi)2Te3. This makes the material ferromagnetic. CREDIT: Hiroshima University |
Abstract:
A group of researchers in Japan and China identified the requirements for the development of new types of extremely low power consumption electric devices by studying Cr-doped (Sb, Bi)2Te3 thin films. This study has been reported in Nature Communications.
A clue to generate electric current without energy consumption at room temperature
Hiroshima, Japan | Posted on December 29th, 2015At extremely low temperatures, an electric current flows around the edge of the film without energy loss, and under no external magnetic field. This attractive phenomenon is due to the material's ferromagnetic properties; however, so far, it has been unclear how the material gains this property. For the first time, researchers have revealed the mechanism by which this occurs. "Hopefully, this achievement will lead to the creation of novel materials that operate at room temperature in the future," said Akio Kimura, a professor at Hiroshima University and a member of the research group.
Their achievement can be traced back to the discovery of the quantum Hall effect in the 1980's, where an electric current flows along an edge (or interface) without energy loss. However, this requires both a large external magnetic field and an extremely low temperature. This is why practical applications have not been possible. Researchers believed that this problem could be overcome with new materials called topological insulators that have ferromagnetic properties such as those found in Cr-doped (Sb, Bi)2Te3.
A topological insulator, predicted in 2005 and first observed in 2007, is neither a metal nor an insulator, and has exotic properties. For example, an electric current is generated only at the surface or the edge of the material, while no electric current is generated inside it. It looks as if only the surface or the edge of the material has metallic properties, while on the inside it is an insulator.
At extremely low temperatures, a thin film made of Cr-doped (Sb, Bi)2Te3 shows a peculiar phenomenon. As the film itself is ferromagnetic, an electric current is spontaneously generated without an external magnetic field and electric current flows only around the edge of the film without energy loss. However, it was previously unknown as to why Cr-doped (Sb, Bi)2Te3 had such ferromagnetic properties that allowed it to generate electric current.
"That's why we selected the material as the object of our study," said Professor Kimura.
Because Cr is a magnetic element, a Cr atom is equivalent to an atomic-sized magnet. The N-S orientations of such atomic-sized magnets tend to be aligned in parallel by the interactions between the Cr atoms. When the N-S orientations of Cr atoms in Cr-doped (Sb, Bi)2Te3 are aligned in parallel, the material exhibits ferromagnetism. However, the interatomic distances between the Cr atoms in the material are, in fact, too long to interact sufficiently to make the material ferromagnetic.
The group found that the non-magnetic element atoms, such as the Sb and Te atoms, mediate the magnetic interactions between Cr atoms and serve as the glue to fix the N-S orientations of Cr atoms that face one direction. In addition, the group expects that its finding will provide a way to increase the critical temperature for relevant device applications.
The experiments for this research were mainly conducted at SPring-8. "We would not have achieved perfect results without the facilities and the staff there. They devoted themselves to detecting the extremely subtle magnetism that the atoms of non-magnetic elements exhibit with extremely high precision. I greatly appreciate their efforts," Kimura said.
Authors and their affiliations:
Mao Ye1,2, Wei Li1,2, Siyuan Zhu3, Yukiharu Takeda4, Yuji Saitoh4, Jiajia Wang5, Hong Pan6, Munisa Nurmamat3, Kazuki Sumida3, Fuhao Ji6, Zhen Liu6, Haifeng Yang1, Zhengtai Liu1, Dawei Shen1,2, Akio Kimura3, Shan Qiao1,2,5, and Xiaoming Xie1,2,5
1 State Key Laboratoryof Functional Materials for Informatics, Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
2 CAS-Shanghai Science Research Center
3 Graduate School of Science, Hiroshima University
4 Condensed Matter Science Division, Quantum Beam Science Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency
5 School of physical science and technology, ShanghaiTech University
6 Department of Physics, State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics, and Laboratory of Advanced Materials, Fudan University
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Norifumi Miyokawa
Copyright © Hiroshima University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








