Home > Press > Magnetic nanoparticle chains offer new technique for controlling soft robots
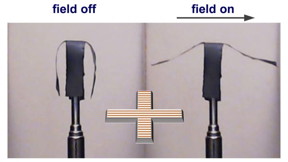 |
| This image shows a selective actuation of the side arms of a soft robot in a horizontal uniform magnetic field. CREDIT: Sumeet Mishra, North Carolina State University |
Abstract:
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a technique for using chains of magnetic nanoparticles to manipulate elastic polymers in three dimensions, which could be used to remotely control new "soft robots."
Magnetic nanoparticle chains offer new technique for controlling soft robots
Raleigh, NC | Posted on December 21st, 2015The ability to control the motion of soft robots, coupled with their flexibility, gives them potential applications ranging from biomedical technologies to manufacturing processes. Researchers are interested in using magnetic fields to control the movement of these soft robots because it can be done remotely - the control can be exerted without physically connecting to the polymer - and because magnetic fields are easily obtained from permanent magnets and electromagnets.
A team of researchers has now found a way of embedding long chains of nanoscale magnetite particles in sheets of elastic polymer to form a magnetic polymer nanocomposite. By applying a magnetic field, the researchers can control the way the nanocomposite bends - making it a soft robot.
The process begins by dispersing nanoparticles of magnetite - an iron oxide - into a solvent. A polymer is then dissolved into the mixture, which is poured into a mold to form the desired shape. A magnetic field is then applied, causing the magnetite nanoparticles to arrange themselves into parallel chains. The solution is dried, locking the chains into place, and the finished nanocomposite can be cut, to further refine its shape.
"Using this technique, we can create large nanocomposites, in many different shapes, which can be manipulated remotely," says Sumeet Mishra, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of a paper on the work. "The nanoparticle chains give us an enhanced response, and by controlling the strength and direction of the magnetic field, you can control the extent and direction of the movements of soft robots."
The mechanism stems from the structure of the chains. The researchers have also constructed a simple model to explain how the chained nanoparticles affect the mechanical response in magnetic fields.
"The key here is that the nanoparticles in the chains and their magnetic dipoles are arranged head-to-tail, with the positive end of one magnetic nanoparticle lined up with the negative end of the next, all the way down the line," says Joe Tracy, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and corresponding author of the paper. "At issue is something called magnetic anisotropy, which is caused by assembling the nanoparticles into chains. When a magnetic field is applied in any direction, the chain re-orients itself to become as parallel as possible to the magnetic field, limited only by the constraints of gravity and the elasticity of the polymer."
The researchers believe this technique may be especially attractive for some biomedical applications, as compared to soft robotics that rely on electricity or light for control. "Electrical control can raise safety issues for some medical applications," says Mishra. "And both electrical and light signals pose challenges in terms of communicating those signals to devices embedded in the body. Magnetic fields, on the other hand, pass through easily - and pose fewer safety challenges."
This technique uses inexpensive and widely available materials, and the process is relatively simple and easy to execute, the researchers say.
###
The paper, "Selective and Directional Actuation of Elastomer Films Using Chained Magnetic Nanoparticles," is published online in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Nanoscale. The paper is co-authored by Michael Dickey and Orlin Velev of NC State's Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The work was supported by the National Science Foundation, under grant DMR-1056653, and by the NSF-funded Research Triangle Materials Research Science and Engineering Center, under grant DMR-1121107.
Mishra won a Gold Graduate Student award from the Materials Research Society in December 2015 for his work on this research effort.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Copyright © Magnetic nanoparticle chains offer new technique for control
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Robotics
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








