Home > Press > Superhydrophobic coating protects without the price: 'Green' project led by Rice, Swansea scientists matches best water repellant
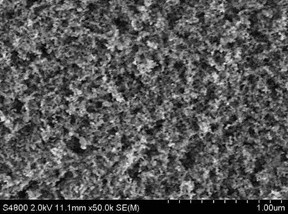 |
| A scanning electron microscope image of a new superhydrophobic material shows the rough surface of functionalized alumina nanoparticles. Scientists at Rice University and the University of Swansea led the creation of the environmentally friendly material. Credit: University of Swansea |
Abstract:
A new class of superhydrophobic nanomaterials might simplify the process of protecting surfaces from water.
Superhydrophobic coating protects without the price: 'Green' project led by Rice, Swansea scientists matches best water repellant
Houston, TX | Posted on December 9th, 2015A material made by scientists at Rice University, the University of Swansea, the University of Bristol and the University of Nice Sophia Antipolis is inexpensive, nontoxic and can be applied to a variety of surfaces via spray- or spin-coating.
The researchers led by Rice chemist Andrew Barron reported their find in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces.
The hydrocarbon-based material may be a "green" replacement for costly, hazardous fluorocarbons commonly used for superhydrophobic applications, Barron said.
"Nature knows how to make these materials and stay environmentally friendly," Barron said. "Our job has been to figure out how and why, and to emulate that."
The lotus leaf was very much on their minds as the researchers tried to mimic one of the most hydrophobic -- water-repelling -- surfaces on the planet. Barron said the leaf's abilities spring from its hierarchy of microscopic and nanoscale double structures.
"In the lotus leaf, these are due to papillae within the epidermis and epicuticular waxes on top," he said. "In our material, there is a microstructure created by the agglomeration of alumina nanoparticles mimicking the papillae and the hyperbranched organic moieties simulating the effect of the epicuticular waxes."
Fabrication and testing of what the researchers call a branched hydrocarbon low-surface energy material (LSEM) were carried out by lead author Shirin Alexander, a research officer at the Energy Safety Research Institute at the Swansea University Bay Campus.
There, Alexander coated easily synthesized aluminum oxide nanoparticles with modified carboxylic acids that feature highly branched hydrocarbon chains. These spiky chains are the first line of defense against water, making the surface rough. This roughness, a characteristic of hydrophobic materials, traps a layer of air and minimizes contact between the surface and water droplets, which allows them to slide off.
To be superhydrophobic, a material has to have a water contact angle larger than 150 degrees. Contact angle is the angle at which the surface of the water meets the surface of the material. The greater the beading, the higher the angle. An angle of 0 degrees is basically a puddle, while a maximum angle of 180 degrees defines a sphere just touching the surface.
The Barron team's LSEM, with an observed angle of about 155 degrees, is essentially equivalent to the best fluorocarbon-based superhydrophobic coatings, Barron said. Even with varied coating techniques and curing temperatures, the material retained its qualities, the researchers reported.
Potential applications include friction-reducing coatings for marine applications where there is international agreement in trying to keep water safe from such potentially dangerous additives as fluorocarbons, Barron said. "The textured surfaces of other superhydrophobic coatings are often damaged and thus reduce the hydrophobic nature," he said. "Our material has a more random hierarchical structure that can sustain damage and maintain its effects."
He said the team is working to improve the material's adhesion to various substrates, as well as looking at large-scale application to surfaces.
Co-authors of the paper are Julian Eastoe, a professor of chemistry at the University of Bristol; Alex Lord, a researcher at the Swansea University Center for Nanohealth; and Frédéric Guittard, a professor at the University of Nice Sophia Antipolis. Barron is the Charles W. Duncan Jr.–Welch Professor of Chemistry and a professor of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice and the Sêr Cymru Chair of Low Carbon Energy and Environment at Swansea.
The Robert A. Welch Foundation and the Welsh Government Sêr Cymru Program supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,888 undergraduates and 2,610 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








