Home > Press > Researchers develop nanoscale probes for ssDNA sustainability under UV radiation: Innovative approach integrating multi-color fluorescence experiments with quantum mechanical theory has great potential for monitoring DNA radiation damage live
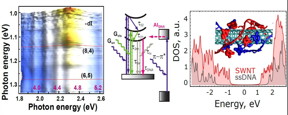 |
| DNA wrapped around nanotube (right inset) is capable to recover after absorbing ultraviolet (UV) radiation by an autoionization process. Experimental two-color fluorescence spectroscopy (left) was combined with quantum mechanical calculations (right and middle inset) to explain the anomalous fluorescence quenching in nanotube under UV illumination.
CREDIT: Slava V. Rotkin, Tetyana Ignatova, Michael Blades, Alexander Balaeff, Ming Zheng and Peter Stoeckl |
Abstract:
DNA, which stores genetic information in the majority of organisms on Earth, is not easily destroyed. It readily absorbs ultraviolet (UV) radiation, but finds ways to recover.
Researchers develop nanoscale probes for ssDNA sustainability under UV radiation: Innovative approach integrating multi-color fluorescence experiments with quantum mechanical theory has great potential for monitoring DNA radiation damage live
Bethlehem, PA | Posted on December 9th, 2015To combat radiation's damage, cells have developed DNA repair mechanisms, as well as mechanisms to remove the energy before it breaks the DNA, such as autoionization, which is the process by which the macro-molecule in an excited state spontaneously emits one of its electrons, releasing a huge amount of energy. Understanding this mechanism is critical to investigating and mitigating the effects of radiation on living organisms.
A team of researchers from Lehigh University (Slava V. Rotkin, Tetyana Ignatova, Michael Blades), the University of Central Florida (Alexander Balaeff), the National Institute of Standards and Technology (Ming Zheng) and a student from the University of Rochester participating in the NSF-Supported "Research Experiences for Undergraduates" (REU) Summer Program at Lehigh (Peter Stoeckl) set out to understand the stability of DNA as a carrier of genetic information against potential damage by UV radiation. They have reported their findings in a paper recently accepted for publication in Nano Research.
Rotkin and his colleagues studied self-assembled complexes of DNA wrapped around single-wall carbon nanotubes utilizing a special technique: two-color photoluminescence spectroscopy. Using the UV and green light simultaneously to probe the sample provided a perspective that no one had been able to observe before in single-color experiments. Later, a quantum mechanical theory was developed to support the experimental data and they were able to confirm a very fast DNA autoionization rate.
"Being able to establish the efficiency of the autoionization process is a key step in understanding how UV-excited DNA can 'cool down' without breaking, thus keeping its normal biological functions," said Rotkin, a professor in Lehigh's Department of Physics and Department of Materials Science & Engineering.
The team's innovative approach has great potential for monitoring DNA excitation, autoionization and chemical damage important for such diverse fields as medicine, evolutionary biology, and space exploration. For biomedical purposes, the ability to study the autoionization mechanism could contribute to an understanding of the survivable levels of UV radiation for different cell types and ways to mitigate irradiation effects. From an evolutionary perspective, it is important to understand the dissipation mechanisms which were crucial during primordial cell evolution when UV radiation was orders of magnitude more intense than today while the DNA repair mechanisms were presumably non-existent. For continued exploration of space, it is important to develop strategies for cellular and organismal safety in harsh radiation conditions.
It took the researchers three years to collect the data and analyze the effects. "We found abnormal behavior of the nanotube emission: it seemed like something was 'stealing' the emitted light under the second-color UV illumination," said Rotkin. "This field is still extremely underexplored. No one had seen this before and we had to hypothesize about the two-color data for a while, putting forward and experimentally rejecting various models in order to find the right interpretation."
It was only when they assumed that the DNA was the source of the observed phenomenon--and rejected a widely accepted model--that the researchers were they able to fully understand nanotube optical quenching.
DNA is very useful for studying nanotubes. A strand of DNA wrapped around a single carbon nanotube-- a miniature cylindrical carbon structure that has a hexagonal graphite lattice and walls that are only one atom thick--will hold the nanotube in water and allow it to have practically the same good optical properties as pristine material.
Initially, the researchers were surprised to observe changes in the nanotube's optical properties as the UV light was applied to the samples.
"For years it has been commonly accepted that DNA is an 'inert' carrier for nanotubes and that DNA holds the nanotube in water without changing its properties," added Rotkin. "It took several years for our team to part with this commonly-held idea, because it was so broadly accepted. Finally, after a series of additional experiments, the data clearly indicated the origin of the modulation to be the DNA itself."
On the heels of this discovery, the researchers have shifted the focus of their project to see how their two-color photoluminescence spectroscopy technique could be used to further probe the properties of DNA.
"It is now understood that different DNA nucleobases show different autoionization properties," concluded Rotkin. "We anticipate this will create unprecedented non-invasive biomolecular tools for solving critical problems of biophysics of nucleic acids."
The study was funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF:ECCS) within the project called "Fundamental physics and biosensing applications of composite fluorescent nanomaterials - rare-earths combined with DNA-enclosed carbon nanotubes."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lori Friedman
610-758-3224
Copyright © Lehigh University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








