Home > Press > IBS reports a high performance nanoparticle electrocatalyst: Scientists from the Center for Nanoparticle Research develop a high performance and cost effective fuel cell
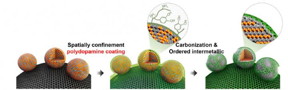 |
| Synthesis of ordered intermetallic fct PtFe/C. Schematic synthesis diagram of carbon-supported and N-doped carbon-coated ordered fct-PtFe NPs. CREDIT: Institute for Basic Science |
Abstract:
Scientists operating out of IBS' Center for Nanoparticle Research have reported highly durable and active intermetallic platinum-iron (PtFe) nanoparticles (NPs) coated with nitrogen (N) doped carbon shell. Precision sized face centered tetragonal (fct) PtFe NPs, only a few nanometers thick, are formed by thermal annealing at 700oC, resulting in a carbon outer layer which protects the NPs from detachment and dissolution throughout the harsh fuel cell operating conditions. The N-doped carbon shell not only prevents the amalgamation of the NPs during a thermal annealing process to keep their sizes as small as 6.5 nm but also protects them under the harsh operating condition.
IBS reports a high performance nanoparticle electrocatalyst: Scientists from the Center for Nanoparticle Research develop a high performance and cost effective fuel cell
Daejeon, Korea | Posted on December 8th, 2015Nanoparticles are microscopic particles between 1 and 100 nanometers (nm) in size. To put that into perspective, the greatest particle size that can pass through a surgical mask is 100 nm. In 1959, physicist Richard Feynman proposed that one day humankind could create machines composed of several individually manipulated molecules or atoms, and these machines could be constructed by tools that were only slightly larger -- an inventive and, for the time, perplexing thought.
Rejuvenated Nano Research
Now, some 40 years later, nanoparticle research has seen something of a renaissance and is an area of intense scientific research, due to a wide variety of potential applications in biomedical, optical, and electronic fields. Published reports have increased exponentially since 2000 and there's little evidence to assume this trend will cease.
Demand for a practical synthetic approach to the high performance electrocatalyst is rapidly increasing for fuel cell commercialization. An electrocatalyst is an electrical current that acts as a catalyst. A fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through an electrochemical reaction of positively charged hydrogen ions with oxygen or another oxidizing agent -- an oxidizing agent or an oxidizer is a chemical species that transfers electronegative atoms, usually oxygen, to a substrate.
These devices are incredibly popular due to their ability to generate electricity by reacting oxygen and hydrogen without emitting CO2. Fuel cells are commonly found in all types of equipment and vehicles, the most common types are found in cars, airplanes, boats and military equipment like submarines and weaponry. There are however limitations to fuel cells: they require platinum which is expensive and found in limited deposits on Earth.
Fuel Cells in Ordinary Life
Nanoparticle-based electrocatalysts have been intensively investigated for fuel cell applications over the past decade, mainly motivated by their high mass activity. Great effort has been exhausted to utilize the high activity and surface area of NPs in order to make a breakthrough for fuel cell commercialization. The team's paper, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, stated that a practical use of nanomaterials for fuel cell electrocatalyst is impeded by their low physical and chemical stability. Under the standard fuel cell operating conditions, NPs are often oxidized, dissolved, or detached from the support and clustered into larger particles, losing their electrochemical catalytic activity during cycling. Therefore, ordered intermetallic NPs are considered as one of the most promising candidates to achieve both high activity and stability in practical fuel cell applications.
The resulting ordered tetragonal-PtFe/ C nanocatalyst coated with an N-doped carbon shell shows the higher performance and durability compared to disordered face centered cubic (fcc)-PtFe/C and commercial Pt/C. According to the team's paper, their approach 'can open a new possibility for the development of high performance and cost effective fuel cell catalysts.' The paper entitled 'Highly Durable and Active PtFe Nanocatalyst for Electrochemical Oxygen Reduction Reaction' is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ms. Sunny Kim
82-428-788-135
Copyright © Institute for Basic Science
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








