Home > Press > Portable device can quickly determine the extent of an eye injury
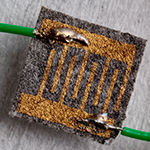 |
| The new sensor can detect differences in vitamin C concentration in fluids that leak from the eye. Higher concentrations indicate a more severe injury, the researchers report.
Photo by L. Brian Stauffer |
Abstract:
n engineer and an ophthalmologist are working together to develop a portable sensor that can quickly and inexpensively determine whether an eye injury is mild or severe. The device, called OcuCheck, works by measuring levels of vitamin C in the fluids that coat or leak from the eye. The sensor could speed efforts to determine the extent of eye injuries at accident sites, in rural areas lacking ophthalmology specialists or on the battlefield, the researchers said.
Portable device can quickly determine the extent of an eye injury
Champaign, IL | Posted on December 8th, 2015“The sensor takes advantage of the fact that the ocular tear film – the viscous fluid that coats the eyeball – contains low levels of ascorbic acid, which is just vitamin C, while the interior of the eye contains much higher levels,” said University of Illinois bioengineering professor Dipanjan Pan, who is creating the device in collaboration with Carle ophthalmologist Dr. Leanne Labriola. “So the concept is, if there is severe damage to the eye that penetrates deeply, the ascorbic acid will leak out in high concentration.”
Two postdoctoral researchers in Pan’s laboratory, Manas Gartia and Santosh Misra, helped develop the new sensor. The researchers report their work in the journal Scientific Reports.
At present, those with eye injuries must find their way to a hospital to have their injuries assessed. The process is often complicated, time-consuming and imprecise, Pan said.
“The new device will change the standard of care for evaluating eye traumas,” Labriola said.
No current techniques for assessing eye injuries involve measurements of ascorbic acid, Pan said. “So this is a one-of-a-kind approach.”
“The idea is that the moment that the ascorbic acid comes in and binds to the ascorbate oxidase, it will pull the polymer out of its interaction with the graphene,” changing the sensor’s electrical properties, Pan said.
In tests with clinical samples from 16 patients undergoing eye surgery, the team found that their sensor could – with high sensitivity, accuracy and specificity – detect a range of ascorbic acid concentrations.
OcuCheck has not yet been tested on samples from trauma patients, Pan said.
“But we have mixed the samples with blood, and the sensor’s sensitivity to ascorbic acid is retained even in the presence of blood. The filter paper will filter out the blood,” he said.
“This technology has the ability to impact a large number of patients, particularly in rural settings, where access to an ophthalmologist can be limited,” Labriola said.
The team is working with an industrial design professor at Illinois to build a housing for the sensor that will be portable and easy to use, Pan said. Pan and Labriola have founded a new company, InnSight Technology, to help them bring the device to market. The company has obtained a phase I Small Business Innovation Research grant from the National Science Foundation.
“This is a perfect example of physicians and engineers working together to find solutions to current problems in health care,” Pan said, referring to the Carle Illinois College of Medicine, a new engineering-based medical college soon to be established on Illinois’ Urbana-Champaign campus.
The University of Illinois and the Children’s Discovery Institute supported this research. Pan also is a faculty member in the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at the U. of I.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Diana Yates
Life Sciences Editor
217-333-5802
Dipanjan Pan
217-244-2938
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








