Home > Press > ORNL microscopy captures real-time view of evolving fuel cell catalysts
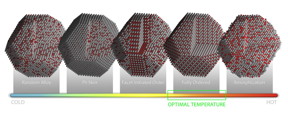 |
| Models of platinum-cobalt nanoparticle catalysts illustrate how specific atomic configurations originate and evolve as the particles are heated.
Illustration by Andy Sproles, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, US Department of Energy. |
Abstract:
Atomic-level imaging of catalysts by scientists at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory could help manufacturers lower the cost and improve the performance of emission-free fuel cell technologies.
ORNL microscopy captures real-time view of evolving fuel cell catalysts
Oak Ridge, TN | Posted on November 21st, 2015Fuel cells rely on costly platinum catalysts to enable the reactions that convert chemical energy into electricity. Alloying platinum with noble metals such as cobalt reduces the overall cost, but such alloyed catalysts vary in performance based on their atomic structure and processing history.
An ORNL team used scanning transmission electron microscopy to track atomic reconfigurations in individual platinum-cobalt nanoparticle catalysts as the particles were heated inside the microscope. The in-situ measurements -- acquired in real time in the vacuum of the microscope column -- allowed the researchers to collect atomic level data that could not be obtained with conventional microscopy techniques. The results are published in Nature Communications.
"This is the first time individual nanoparticles have been tracked this way -- to image the structural and compositional changes at the atomic level from the start of an annealing process to the finish," ORNL coauthor Karren More said.
Very small changes in the positions of platinum and cobalt atoms affect the catalyst's overall activity and selectivity, so annealing -- a gradual heating, holding, and cooling process -- is often used to modify the alloy's surface structure. The ORNL in situ microscopy experiments documented exactly what, when and how specific atomic configurations originate and evolve during the annealing process.
"You can anneal something from room temperature to 800 degrees Celsius, but you don't know at which point you should stop the process to ensure the best catalytic performance," lead author Miaofang Chi said. "Because you don't know how the particle evolves, you might be missing the optimum surface configuration."
The atomic-level detail in the ORNL study will guide researchers and manufacturers who want to fine-tune their catalysts' atomic structure to meet the demands of a specific application.
"This work paves the way towards designing catalysts through post-synthesis annealing for optimized performance," Chi said.
###
The study is published as "Surface faceting and elemental diffusion behavior at atomic scale for alloy nanoparticles during in situ annealing." Coauthors are ORNL's Miaofang Chi, Karren More, Andrew Lupini and Lawrence Allard; Johns Hopkins University's Chao Wang; University of Pittsburgh's Yinkai Lei and Guofeng Wang; and Argonne National Laboratory's Dongguo Li, Nenad Markovic, and Vojislav Stamenkovic.
The research was sponsored by the Fuel Cell Technologies Office in DOE's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, and microscopy was performed at ORNL's Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, a DOE Office of Science User Facility.
####
About Oak Ridge National Laboratory
ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle for the Department of Energy's Office of Science. DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Morgan McCorkle
865-574-7308
Copyright © Oak Ridge National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








