Home > Press > Strange quantum phenomenon achieved at room temperature in semiconductor wafers
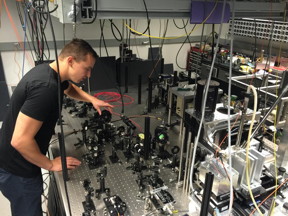 |
| Paul Klimov, a graduate student in the University of Chicago's Institute for Molecular Engineering, adjusts the intensity of a laser beam during an experiment. Because the laser light lies within the infrared spectrum, it is invisible to the human eye. CREDIT: University of Chicago |
Abstract:
Entanglement is one of the strangest phenomena predicted by quantum mechanics, the theory that underlies most of modern physics. It says that two particles can be so inextricably connected that the state of one particle can instantly influence the state of the other, no matter how far apart they are.
Strange quantum phenomenon achieved at room temperature in semiconductor wafers
Chicago, IL | Posted on November 21st, 2015Just one century ago, entanglement was at the center of intense theoretical debate, leaving scientists like Albert Einstein baffled. Today, however, entanglement is accepted as a fact of nature and is actively being explored as a resource for future technologies including quantum computers, quantum communication networks, and high-precision quantum sensors.
Entanglement is also one of nature's most elusive phenomena. Producing entanglement between particles requires that they start out in a highly ordered state, which is disfavored by thermodynamics, the process that governs the interactions between heat and other forms of energy. This poses a particularly formidable challenge when trying to realize entanglement at the macroscopic scale, among huge numbers of particles.
"The macroscopic world that we are used to seems very tidy, but it is completely disordered at the atomic scale. The laws of thermodynamics generally prevent us from observing quantum phenomena in macroscopic objects," said Paul Klimov, a graduate student in the University of Chicago's Institute for Molecular Engineering and lead author of new research on quantum entanglement. The institute is a partnership between UChicago and Argonne National Laboratory.
Previously, scientists have overcome the thermodynamic barrier and achieved macroscopic entanglement in solids and liquids by going to ultra-low temperatures (-270 degrees Celsius) and applying huge magnetic fields (1,000 times larger than that of a typical refrigerator magnet) or using chemical reactions. In the Nov. 20 issue of Science Advances, Klimov and other researchers in David Awschalom's group at the Institute for Molecular Engineering have demonstrated that macroscopic entanglement can be generated at room temperature and in a small magnetic field.
The researchers used infrared laser light to order (preferentially align) the magnetic states of thousands of electrons and nuclei and then electromagnetic pulses, similar to those used for conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to entangle them. This procedure caused pairs of electrons and nuclei in a macroscopic 40 micrometer-cubed volume (the volume of a red blood cell) of the semiconductor SiC to become entangled.
"We know that the spin states of atomic nuclei associated with semiconductor defects have excellent quantum properties at room temperature," said Awschalom, Liew Family Professor in Molecular Engineering and a senior scientist at Argonne National Laboratory. "They are coherent, long-lived and controllable with photonics and electronics. Given these quantum 'pieces,' creating entangled quantum states seemed like an attainable goal."
In addition to being of fundamental physical interest, "the ability to produce robust entangled states in an electronic-grade semiconductor at ambient conditions has important implications on future quantum devices," Awschalom said.
In the short-term, the techniques used here in combination with sophisticated devices enabled by advanced SiC device-fabrication protocols could enable quantum sensors that use entanglement as a resource for beating the sensitivity limit of traditional (non-quantum) sensors. Given that the entanglement works at ambient conditions and the fact that SiC is bio-friendly, one particularly exciting application is biological sensing inside a living organism.
"We are excited about entanglement-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging probes, which could have important biomedical applications," said Abram Falk of IBM's Thomas J. Watson Research Center and a co-author of the research findings.
In the long term, it might even be possible to go from entangled states on the same SiC chip to entangled states across distant SiC chips. Such efforts could be facilitated by physical phenomena that allow macroscopic quantum states, as opposed to single quantum states (in single atoms), to interact very strongly with one another, which is important for producing entanglement with a high success rate. Such long-distance entangled states have been proposed for synchronizing global positioning satellites and for communicating information in a manner that is fundamentally secured from eavesdroppers by the laws of physics.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Steve Koppes
773-702-8366
Copyright © University of Chicago
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








