Home > Press > Imitating synapses of the human brain could lead to smarter electronics
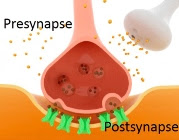 |
| Connections, or synapses, between neurons are inspiring scientists to create artificial versions that could lead to smarter electronics. Credit: American Chemical Society |
Abstract:
Making a computer that learns and remembers like a human brain is a daunting challenge. The complex organ has 86 billion neurons and trillions of connections -- or synapses -- that can grow stronger or weaker over time. But now scientists report in ACS' journal Nano Letters the development of a first-of-its-kind synthetic synapse that mimics the plasticity of the real thing, bringing us one step closer to human-like artificial intelligence.
Imitating synapses of the human brain could lead to smarter electronics
Washington, DC | Posted on November 15th, 2015While the brain still holds many secrets, one thing we do know is that the flexibility, or plasticity, of neuronal synapses is a critical feature. In the synapse, many factors, including how many signaling molecules get released and the timing of release, can change. This mutability allows neurons to encode memories, learn and heal themselves. In recent years, researchers have been building artificial neurons and synapses with some success but without the flexibility needed for learning. Tian-Ling Ren and colleagues set out to address that challenge.
The researchers created an artificial synapse out of aluminum oxide and twisted bilayer graphene. By applying different electric voltages to the system, they found they could control the reaction intensity of the receiving "neuron." The team says their novel dynamic system could aid in the development of biology-inspired electronics capable of learning and self-healing.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Basic Research Program of China, the National Key Project of Science and Technology and the Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest of China.
####
About American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 158,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Bernstein
202-872-6042
Tian-Ling Ren, Ph.D.
Institute of Microelectronics
and Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology (TNList)
Tsinghua University
Beijing, China
Copyright © American Chemical Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() DOWNLOAD FULL-TEXT ARTICLE - "Graphene Dynamic Synapse with Modulatable Plasticity":
DOWNLOAD FULL-TEXT ARTICLE - "Graphene Dynamic Synapse with Modulatable Plasticity":
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Synthetic Biology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Artificial Intelligence
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
![]() Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








