Home > Press > Engineers design magnetic cell sensors: New protein nanoparticles allow scientists to track cells and interactions within them
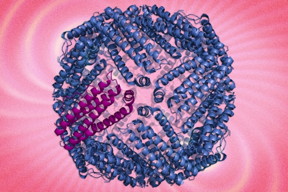 |
| hown here is a ferritin protein complex. MIT researchers are using protein engineering the boost the magnetic characteristics of the protein to track cells.
Illustration: Jose-Luis Olivares/MIT (ferritin illustrations courtesy of Wikimedia) |
Abstract:
MIT engineers have designed magnetic protein nanoparticles that can be used to track cells or to monitor interactions within cells. The particles, described today in Nature Communications, are an enhanced version of a naturally occurring, weakly magnetic protein called ferritin.
Engineers design magnetic cell sensors: New protein nanoparticles allow scientists to track cells and interactions within them
Cambridge, MA | Posted on November 2nd, 2015"Ferritin, which is as close as biology has given us to a naturally magnetic protein nanoparticle, is really not that magnetic. That's what this paper is addressing," says Alan Jasanoff, an MIT professor of biological engineering and the paper's senior author. "We used the tools of protein engineering to try to boost the magnetic characteristics of this protein."
The new "hypermagnetic" protein nanoparticles can be produced within cells, allowing the cells to be imaged or sorted using magnetic techniques. This eliminates the need to tag cells with synthetic particles and allows the particles to sense other molecules inside cells.
The paper's lead author is former MIT graduate student Yuri Matsumoto. Other authors are graduate student Ritchie Chen and Polina Anikeeva, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering.
Magnetic pull
Previous research has yielded synthetic magnetic particles for imaging or tracking cells, but it can be difficult to deliver these particles into the target cells.
In the new study, Jasanoff and colleagues set out to create magnetic particles that are genetically encoded. With this approach, the researchers deliver a gene for a magnetic protein into the target cells, prompting them to start producing the protein on their own.
"Rather than actually making a nanoparticle in the lab and attaching it to cells or injecting it into cells, all we have to do is introduce a gene that encodes this protein," says Jasanoff, who is also an associate member of MIT's McGovern Institute for Brain Research.
As a starting point, the researchers used ferritin, which carries a supply of iron atoms that every cell needs as components of metabolic enzymes. In hopes of creating a more magnetic version of ferritin, the researchers created about 10 million variants and tested them in yeast cells.
After repeated rounds of screening, the researchers used one of the most promising candidates to create a magnetic sensor consisting of enhanced ferritin modified with a protein tag that binds with another protein called streptavidin. This allowed them to detect whether streptavidin was present in yeast cells; however, this approach could also be tailored to target other interactions.
Sensing cell signals
Because the engineered ferritins are genetically encoded, they can be manufactured within cells that are programmed to make them respond only under certain circumstances, such as when the cell receives some kind of external signal, when it divides, or when it differentiates into another type of cell. Researchers could track this activity using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), potentially allowing them to observe communication between neurons, activation of immune cells, or stem cell differentiation, among other phenomena.
Such sensors could also be used to monitor the effectiveness of stem cell therapies, Jasanoff says.
"As stem cell therapies are developed, it's going to be necessary to have noninvasive tools that enable you to measure them," he says. Without this kind of monitoring, it would be difficult to determine what effect the treatment is having, or why it might not be working.
The researchers are now working on adapting the magnetic sensors to work in mammalian cells. They are also trying to make the engineered ferritin even more strongly magnetic.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah McDonnell
617-253-8923
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








