Home > Press > Umbrella-shaped diamond nanostructures make efficient photon collectors: Umbrella-shaped diamond nanostructures make efficient photon collectors
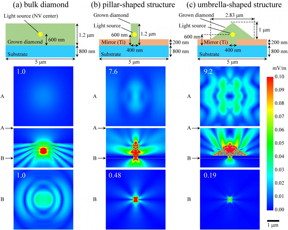 |
| These are schematic images of analyzed objects and electric field maps calculated by FDTD simulations of (a) bulk diamond, (b) pillar-shaped structures, and (c) umbrella-shaped structures. Cross-sectional schematics, planar field maps at the height A, cross-sectional maps, and planar maps at the height B are shown from top to bottom. CREDIT: M. Hatano, et al. |
Abstract:
Standard umbrellas come out when the sky turns dark, but in the nanoworld, umbrella shapes may be the next creative way to enhance light emission. Inspired by recent work to enhance the luminescence from diamond nanopillar structures, a team of researchers in Japan has discovered that "umbrella-shaped" diamond nanostructures with metal mirrors on the bottom are more efficient photon collectors than their diamond nanostructure "cousins" of other shapes.
Umbrella-shaped diamond nanostructures make efficient photon collectors: Umbrella-shaped diamond nanostructures make efficient photon collectors
Washington, DC | Posted on October 21st, 2015By tweaking the shape of the diamond nanostructures into the form of tiny umbrellas, researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology experimentally showed that the fluorescence intensity of their structures was three to five times greater than that of bulk diamond. They report their results in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
To get started, the team formed the umbrella-shaped diamond nanostructures by using an original "bottom-up" fabrication technique that relies on selective and anisotropic growth through holes in a metal mask. The metal mask also serves as a mirror that is self-aligned to the diamond nanostructures.
"Our umbrella-shaped nanostructure has an effect similar to a solid immersion lens, which reduces the chance of total reflection on its upper surface and focuses the emitted light toward the 'upside' of the structure," explained Mutsuko Hatano, a professor in the Graduate School of Science and Engineering's Department of Physical Electronics at Tokyo Institute of Technology.
The self-aligned mirror goes a step further to enhance the efficiency of collecting this light by reflecting it at the lower surface area of the nanostructure.
"Umbrella-shaped diamond provides significantly better photon collection efficiency than bulk diamond or its pillar-shaped diamond counterpart, which have already been studied extensively," Hatano noted.
The significance of the team's discovery is that they've shown that the brighter fluorescence intensity of umbrella-shaped diamond nanostructures can be achieved by improving the photon collection efficiency of the nitrogen vacancy centers, which are the numerous point defects in diamonds that happen to boast the property of photoluminescence.
These nitrogen vacancy centers possess unique properties such as optical initialization and detection of its spin states, stable and strong fluorescence even from a single center, and long spin coherence time at room temperature. These properties make nitrogen vacancy centers in diamonds candidates for next-generation spin-based quantum devices such as magnetometers, quantum computers, and for research or work involving biological observations. Individual nitrogen vacancy centers could essentially function as the basic units of quantum computers.
Brighter fluorescence intensity is an essential aspect of improving the photon collection efficiency from nitrogen vacancy centers. Due to the high refractive index (2.4) of diamond, the photon collection efficiency from the nitrogen vacancy centers in bulk diamond is low. "In other words, diamond works as an effective light waveguide in low-refractive-index environments," said Hatano.
In terms of applications, the team's nanostructures may find use in highly sensitive magnetic sensors for making biological observations or within the computational science realm for quantum computing and cryptographic communications.
Next, Hatano and colleagues plan to pursue better control of the nanostructures' shape, as well as target a smoother surface by optimizing chemical vapor deposition growth conditions.
"Our goal now is to improve the nanostructures' photon collection efficiency," she said. "We also plan to demonstrate quantum sensors -- in particular, highly sensitive magnetometers intended for life science and medical applications."
The authors of this paper are affiliated with Tokyo Institute of Technology. The work was supported by CREST, Japan Science and Technology Agency.
####
About American Institute of Physics
Applied Physics Letters features concise, rapid reports on significant new findings in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology. See: apl.aip.org
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








