Home > Press > Nanoelectronics could get a boost from carbon research: The smallest of electronics could one day have the ability to turn on and off on an atomic scale
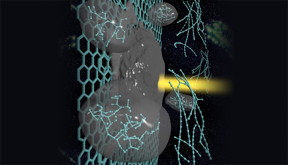 |
| A carbyne strand forms in laser-melted graphite. Carbyne is found in astrophysical bodies and has the potential to be used in nanoelectronic devices and superhard materials. Image by Liam Krauss/LLNL |
Abstract:
Lawrence Livermore scientists have investigated a way to create linear chains of carbon atoms from laser-melted graphite. The material, called carbyne, could have a number of novel properties, including the ability to adjust the amount of electrical current traveling through a circuit, depending on the user's needs.
Nanoelectronics could get a boost from carbon research: The smallest of electronics could one day have the ability to turn on and off on an atomic scale
Livermore, CA | Posted on September 17th, 2015Carbyne is the subject of intense research because of its presence in astrophysical bodies, as well as its potential use in nanoelectronic devices and superhard materials. Its linear shape gives it unique electrical properties that are sensitive to stretching and bending, and it is 40 times stiffer than diamond. It also was found in the Murchison and Allende meteorites and could be an ingredient of interstellar dust.
Using computer simulations, LLNL scientist Nir Goldman and colleague Christopher Cannella (an undergraduate summer researcher from Caltech) initially intended to study the properties of liquid carbon as it evaporates, after being formed by shining a laser beam on the surface of graphite. The laser can heat the graphite surface to a few thousands of degrees, which then forms a fairly volatile droplet. To their surprise, as the liquid droplet evaporated and cooled in their simulations, it formed bundles of linear chains of carbon atoms.
"There's been a lot of speculation about how to make carbyne and how stable it is," Goldman said. "We showed that laser melting of graphite is one viable avenue for its synthesis. If you regulate carbyne synthesis in a controlled way, it could have applications as a new material for a number of different research areas, including as a tunable semiconductor or even for hydrogen storage.
"Our method shows that carbyne can be formed easily in the laboratory or otherwise. The process also could occur in astrophysical bodies or in the interstellar medium, where carbon containing material can be exposed to relatively high temperatures and carbon can liquefy."
Goldman's study and computational models allow for direct comparison with experiments and can help determine parameters for synthesis of carbon-based materials with potentially exotic properties.
"Our simulations indicate a possible mechanism for carbyne fiber synthesis that confirms previous experimental observation of its formation," Goldman said. "These results help determine one set of thermodynamic conditions for its synthesis and could account for its detection in meteorites resulting from high-pressure conditions due to impact."
###
The research appears on the cover of the Sept. 17 edition of the Journal of Physical Chemistry.
####
About DOE/Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory provides solutions to our nation's most important national security challenges through innovative science, engineering and technology. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anne Stark
925-422-9799
Copyright © DOE/Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








