Home > Press > Reversible Writing with Light: Self-assembling nanoparticles take their cues from their surroundings
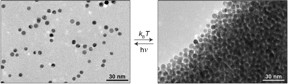 |
| Nanoparticles in a light-sensitive medium scatter in the light (left) and aggregate in the dark (right). This method could be the basis of future-quot; re-writable paper-quot. CREDIT: Weizmann Institute of Science |
Abstract:
The medium is the message. Dr. Rafal Klajn of the Weizmann Institute's Organic Chemistry Department and his group have given new meaning to this maxim: An innovative method they have now demonstrated for getting nanoparticles to self-assemble focuses on the medium in which the particles are suspended; these assemblies can be used, among other things, for reversibly writing information.
Reversible Writing with Light: Self-assembling nanoparticles take their cues from their surroundings
Rehovot, Israel | Posted on September 3rd, 2015This approach is an elegant alternative to present methods that require nanoparticles to be coated with light-sensitive molecules; these then switch the particles' state when light is shined on them. According to the group's research, which recently appeared in Nature Chemistry, putting regular, uncoated nanoparticles into a light-sensitive medium would be simpler, and the resulting system more efficient and durable than existing ones. The possible applications range from rewritable paper, to water decontamination, to the controlled delivery of drugs or other substances.
The medium, in this case, is made up of small "photo-switchable" (or "photoresponsive") molecules called spiropyrans. In the version of the photoresponsive molecule employed by Klajn and his group, absorbing light switches the molecule to a form that is more acidic. The nanoparticles then react to the change in acidity in their environment: It is this reaction that causes the particles to aggregate in the dark and disperse in the light. This means that any nanoparticles that respond to acid - a much larger group than those that respond to light - can now potentially be manipulated into self-assembly.
By using light - a favored means of generating nanoparticle self-assembly - to control the reaction, one can precisely govern when and where the nanoparticles will aggregate. And since nanoparticles tend to have different properties if they are floating freely or clustered together, the possibilities for creating new applications are nearly limitless.
Klajn points out that these molecules have a long history at the Weizmann Institute: "Two Institute scientists, Ernst Fischer and Yehuda Hirshberg, were the first to demonstrate the light-responsive behavior of spiropyrans in 1952. Later on, in the 1980s, Prof. Valeri Krongauz used these molecules to develop a variety of materials including photosensitive coatings for lenses. Now, 63 years after the first demonstration of its light-responsive properties, we are using the same simple molecule for another use, entirely," he says.
The advantages of the medium-based approach are clear. For one, the particles do not seem to degrade over time - a problem that plagues the coated nanoparticles. "We ran one hundred cycles of writing and rewriting with the nanoparticles in a gel-like medium - what we call reversible information storage - and there was no deterioration in the system. So you could use the same system over and over again," says Klajn. "And, although we used gold nanoparticles for our experiments, theoretically one could even use sand, as long as it was sensitive to changes in acidity."
In addition to durable "rewritable paper," Klajn suggests that future applications of this method might include removing pollutants from water - certain nanoparticles can aggregate around contaminants and release them later on demand - as well as the controlled delivery of tiny amounts of substances, for example, drugs, that could be released with light.
###
Dr. Rafal Klajn's research is supported by the Abramson Family Center for Young Scientists; the Rothschild Caesarea Foundation; the Mel and Joyce Eisenberg-Keefer Fund for New Scientists; the estate of Olga Klein Astrachan; and the European Research Council.
####
About Weizmann Institute of Science
The Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel, is one of the world's top-ranking multidisciplinary research institutions. Noted for its wide-ranging exploration of the natural and exact sciences, the Institute is home to scientists, students, technicians and supporting staff. Institute research efforts include the search for new ways of fighting disease and hunger, examining leading questions in mathematics and computer science, probing the physics of matter and the universe, creating novel materials and developing new strategies for protecting the environment.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yael Edelman
Copyright © Weizmann Institute of Science
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








