Home > Press > Successful boron-doping of graphene nanoribbon
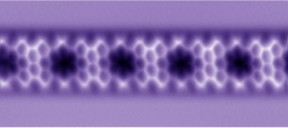 |
| Graphene nanoribbon under the microscope. Image: University of Basel |
Abstract:
Physicists at the University of Basel succeed in synthesizing boron-doped graphene nanoribbons and characterizing their structural, electronic and chemical properties. The modified material could potentially be used as a sensor for the ecologically damaging nitrogen oxides, scientists report in the latest issue of Nature Communications.
Successful boron-doping of graphene nanoribbon
Basel, Switzerland | Posted on August 27th, 2015Graphene is one of the most promising materials for improving electronic devices. The two-dimensional carbon sheet exhibits high electron mobility and accordingly has excellent conductivity. Other than usual semiconductors, the material lacks the so-called band gap, an energy range in a solid where no electron states can exist. Therefore, it avoids a situation in which the device is electronically switched off. However, in order to fabricate efficient electronic switches from graphene, it is necessary that the material can be switched "on" and "off".
The solution to this problem lies in trimming the graphene sheet to a ribbon-like shape, named graphene nanoribbon (GNR). Thereby it can be altered to have a band gap whose value is dependent on the width of the shape.
Synthesis on Gold Surface
To tune the band gap in order for the graphene nanoribbons to act like a well-established silicon semiconductor, the ribbons are being doped. To that end, the researchers intentionally introduce impurities into pure material for the purpose of modulating its electrical properties. While nitrogen doping has been realized, boron-doping has remained unexplored. Subsequently, the electronic and chemical properties have stayed unclear thus far.
Prof. Dr. Ernst Meyer and Dr. Shigeki Kawai from the Department of Physics at the University of Basel, assisted by researchers from Japanese and Finnish Universities, have succeeded in synthesizing boron-doped graphene nanoribbons with various widths. They used an on-surface chemical reaction with a newly synthesized precursor molecule on an atomically clean gold surface. The chemical structures were directly resolved by state-of-the-art atomic force microscopy at low temperature.
Towards a Nitrogen Oxide-Sensor
The doped site of the boron atom was unambiguously confirmed and its doping ratio - the number of boron atoms relative to the total number of atoms within the nanoribbon - lay at 4.8 atomic percent. By dosing nitric oxide gas, the chemical property known as the Lewis acidity could also be confirmed.
The doped nitric oxide gas was highly-selectively adsorbed on the boron site. This measurement indicates that the boron-doped graphene nanoribbon can be used for an ultra-high sensitive gas sensor for nitrogen oxides which are currently a hot topic in the industry as being highly damaging to the environment.
###
Original Source
S. Kawai, S. Saito, O. Oshima, S. Yamaguchi, A. S. Foster, P. Spiker, and E. Meyer
Atomically controlled substitutional boron-doping of graphene nanoribbons
Nature Communications, 6. 8098 (2015), doi: 10.1038/ncomms9098
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Olivia Poisson
Copyright © University of Basel
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








