Home > Press > Sol-gel capacitor dielectric offers record-high energy storage
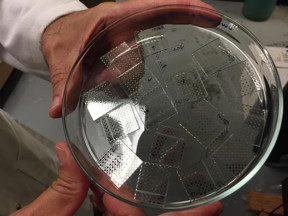 |
| These are samples of the new hybrid sol-gel material are shown placed on a clear plastic substrate for testing.
Credit: John Toon, Georgia Tech |
Abstract:
Using a hybrid silica sol-gel material and self-assembled monolayers of a common fatty acid, researchers have developed a new capacitor dielectric material that provides an electrical energy storage capacity rivaling certain batteries, with both a high energy density and high power density.
Sol-gel capacitor dielectric offers record-high energy storage
Atlanta, GA | Posted on July 30th, 2015If the material can be scaled up from laboratory samples, devices made from it could surpass traditional electrolytic capacitors for applications in electromagnetic propulsion, electric vehicles and defibrillators. Capacitors often complement batteries in these applications because they can provide large amounts of current quickly.
The new material is composed of a silica sol-gel thin film containing polar groups linked to the silicon atoms and a nanoscale self-assembled monolayer of an octylphosphonic acid, which provides insulating properties. The bilayer structure blocks the injection of electrons into the sol-gel material, providing low leakage current, high breakdown strength and high energy extraction efficiency.
"Sol-gels with organic groups are well known and fatty acids such as phosphonic acids are well known," noted Joseph Perry, a professor in the School of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the Georgia Institute of Technology. "But to the best of our knowledge, this is the first time these two types of materials have been combined into high-density energy storage devices."
The research, supported by the Office of Naval Research and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, was reported July 14 in the journal Advanced Energy Materials.
The need for efficient, high-performance materials for electrical energy storage has been growing along with the ever-increasing demand for electrical energy in mobile applications. Dielectric materials can provide fast charge and discharge response, high energy storage, and power conditioning for defense, medical and commercial applications. But it has been challenging to find a single dielectric material able to maximize permittivity, breakdown strength, energy density and energy extraction efficiency.
Perry and colleagues in Georgia Tech's Center for Organic Photonics and Electronics (COPE) had been working on other capacitor materials to meet these demands, but were not satisfied with the progress. The hybrid sol-gel materials had shown potential for efficient dielectric energy storage because of their high orientational polarization under an electric field, so the group decided to pursue these materials for the new capacitor applications.
Using an aluminized mylar film coated with the hybrid sol-gel capacitor material, they showed that the capacitor could be rolled and re-rolled several times while maintaining high energy density, demonstrating its flexibility. But they were still seeing high current leakage. To address that, they deposited a nanoscale self-assembled monolayer of n-octylphosphonic acid on top of the hybrid sol-gel. Less than a nanometer thick, the monolayer serves as an insulating layer.
"Our silica sol-gel is a hybrid material because it has polar organic groups attached to the silica framework that gives the sol-gel a high dielectric constant, and in our bilayer dielectric, the n-octylphosphonic acid groups are inserted between the sol-gel layer and the top aluminum layer to block charge injection into the sol-gel," Perry explained. "It's really a bilayer hybrid material that takes the best of both reorientation polarization and approaches for reducing injection and improving energy extraction."
In their structures, the researchers demonstrated maximum extractable energy densities up to 40 joules per cubic centimeter, an energy extraction efficiency of 72 percent at a field strength of 830 volts per micron, and a power density of 520 watts per cubic centimeter. The performance exceeds that of conventional electrolytic capacitors and thin-film lithium ion batteries, though it doesn't match the lithium ion battery formats commonly used in electronic devices and vehicles.
"This is the first time I've seen a capacitor beat a battery on energy density," said Perry. "The combination of high energy density and high power density is uncommon in the capacitor world."
Researchers in Perry's lab have been making arrays of small sol-gel capacitors in the lab to gather information about the material's performance. The devices are made on small substrates about an inch square.
"What we see when we apply an electric field is that the polarization response - which measures how much the polar groups line up in a stable way with the field - behaves in a linear way," said Perry. "This is what you want to see in a capacitor dielectric material."
The next step will be to scale up the materials to see if the attractive properties transfer to larger devices. If that is successful, Perry expects to commercialize the material through a startup company or SBIR project.
"The simplicity of fully solution-based processes for our dielectric material system provides potential for facile scale-up and fabrication on flexible platforms," the authors wrote in their paper. "This work emphasizes the importance of controlling the electrode-dielectric interface to maximize the performance of dielectric materials for energy storage application."
###
In addition to Perry, the research team included Yunsang Kim, Mohanalingam Kathaperumal and Vincent Chen from the Georgia Tech School of Chemistry and Biochemistry; Yohan Park from the Georgia Tech School of Materials Science and Engineering; Canek Fuentes-Hernandez and Bernard Kippelen from the Georgia Tech School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Ming-Hen Pan from the Naval Research Laboratory.
This research was supported by the Office of Naval Research Dielectric Films Program (Grant N000141110462) and U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research, BioPAINTS MURI Program (Grant FA9550-09-0669). The content of this article is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the sponsoring agencies.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
John Toon
404-894-6986
Copyright © Georgia Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








