Home > Press > Superfast fluorescence sets new speed record: Plasmonic device has speed and efficiency to serve optical computers
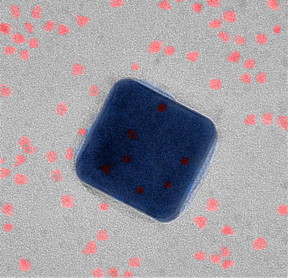 |
| A nanoscale view of the new superfast fluorescent system using a transmission electron microscope. The silver cube is just 75-nanometers wide. The quantum dots (red) are sandwiched between the silver cube and a thin gold foil. CREDIT: Maiken Mikkelsen, Duke University |
Abstract:
Researchers have developed an ultrafast light-emitting device that can flip on and off 90 billion times a second and could form the basis of optical computing.
Superfast fluorescence sets new speed record: Plasmonic device has speed and efficiency to serve optical computers
Durham, NC | Posted on July 27th, 2015At its most basic level, your smart phone's battery is powering billions of transistors using electrons to flip on and off billions of times per second. But if microchips could use photons instead of electrons to process and transmit data, computers could operate even faster.
But first engineers must build a light source that can be turned on and off that rapidly. While lasers can fit this requirement, they are too energy-hungry and unwieldy to integrate into computer chips.
Duke University researchers are now one step closer to such a light source. In a new study, a team from the Pratt School of Engineering pushed semiconductor quantum dots to emit light at more than 90 billion gigahertz. This so-called plasmonic device could one day be used in optical computing chips or for optical communication between traditional electronic microchips.
The study was published online on July 27 in Nature Communications.
"This is something that the scientific community has wanted to do for a long time," said Maiken Mikkelsen, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering and physics at Duke. "We can now start to think about making fast-switching devices based on this research, so there's a lot of excitement about this demonstration."
The new speed record was set using plasmonics. When a laser shines on the surface of a silver cube just 75 nanometers wide, the free electrons on its surface begin to oscillate together in a wave. These oscillations create their own light, which reacts again with the free electrons. Energy trapped on the surface of the nanocube in this fashion is called a plasmon.
The plasmon creates an intense electromagnetic field between the silver nanocube and a thin sheet of gold placed a mere 20 atoms away. This field interacts with quantum dots -- spheres of semiconducting material just six nanometers wide -- that are sandwiched in between the nanocube and the gold. The quantum dots, in turn, produce a directional, efficient emission of photons that can be turned on and off at more than 90 gigahertz.
"There is great interest in replacing lasers with LEDs for short-distance optical communication, but these ideas have always been limited by the slow emission rate of fluorescent materials, lack of efficiency and inability to direct the photons," said Gleb Akselrod, a postdoctoral research in Mikkelsen's laboratory. "Now we have made an important step towards solving these problems."
"The eventual goal is to integrate our technology into a device that can be excited either optically or electrically," said Thang Hoang, also a postdoctoral researcher in Mikkelsen's laboratory. "That's something that I think everyone, including funding agencies, is pushing pretty hard for."
The group is now working to use the plasmonic structure to create a single photon source -- a necessity for extremely secure quantum communications -- by sandwiching a single quantum dot in the gap between the silver nanocube and gold foil. They are also trying to precisely place and orient the quantum dots to create the fastest fluorescence rates possible.
Aside from its potential technological impacts, the research demonstrates that well-known materials need not be limited by their intrinsic properties.
"By tailoring the environment around a material, like we've done here with semiconductors, we can create new designer materials with almost any optical properties we desire," said Mikkelsen. "And that's an emerging area that's fascinating to think about."
###
This work was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research Young Investigator Program (AFOSR, Grant. No. FA9550-15-1-0301), the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR, Grant No. FA9550-12-1-0491), an Oak Ridge Associated University's Ralph E. Powe Junior Faculty Enhancement Award, the Lord Foundation of North Carolina, and the Intelligence Community Postdoctoral Research Fellowship Program.
"Ultrafast Spontaneous Emission Source Using Plasmonic Nanoantennas." Thang B. Hoang, Gleb M. Akselrod, Christos Argyropoulos, Jiani Huang, David R. Smith & Maiken H. Mikkelsen. Nature Communications, July 27, 2015. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8788
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ken Kingery
919-660-8414
Copyright © Duke University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








