Home > Press > Toward nanorobots that swim through blood to deliver drugs (video)
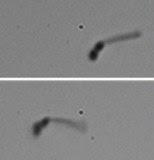 |
| Patients could one day benefit from swimming nanorobots that deliver drugs where they're needed. Credit: American Chemical Society |
Abstract:
Someday, treating patients with nanorobots could become standard practice to deliver medicine specifically to parts of the body affected by disease. But merely injecting drug-loaded nanoparticles might not always be enough to get them where they need to go. Now scientists are reporting in the ACS journal Nano Letters the development of new nanoswimmers that can move easily through body fluids to their targets.
Toward nanorobots that swim through blood to deliver drugs (video)
Washington, DC | Posted on June 17th, 2015Tiny robots could have many benefits for patients. For example, they could be programmed to specifically wipe out cancer cells, which would lower the risk of complications, reduce the need for invasive surgery and lead to faster recoveries. It's a burgeoning field of study with early-stage models currently in development in laboratories. But one of the challenges to making these robots work well is getting them to move through body fluids, which are like molasses to something as small as a nanorobot. Bradley J. Nelson, Salvador Pané, Yizhar Or and colleagues wanted to address this problem.
The researchers strung together three links in a chain about as long as a silk fiber is wide. One segment was a polymer, and two were magnetic, metallic nanowires. They put the tiny devices in a fluid even thicker than blood. And when they applied an oscillating magnetic field, the nanoswimmer moved in an S-like, undulatory motion at the speed of nearly one body length per second. The magnetic field also can direct the swimmers to reach targets.
The authors acknowledge funding from the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme, the European Research Council, the Israel Science Foundation.
####
About American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 158,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Bradley J. Nelson, Ph.D.
Institute of Robotics and Intelligent Systems
ETH Zurich
Zurich, Switzerland
or
Salvador Pané, Ph.D.
Institute of Robotics and Intelligent Systems
ETH Zurich
Zurich, Switzerland
or
Yizhar Or, Ph.D.
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Technion - Israel Institute of Technology
Haifa, Israel
General Inquiries:
Michael Bernstein
202-872-6042
Science Inquiries:
Katie Cottingham, Ph.D.
301-775-8455
Copyright © American Chemical Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() DOWNLOAD FULL-TEXT ARTICLE - "Undulatory Locomotion of Magnetic Multilink Nanoswimmers"
DOWNLOAD FULL-TEXT ARTICLE - "Undulatory Locomotion of Magnetic Multilink Nanoswimmers"
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Robotics
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








