Home > Press > A KAIST research team develops the first flexible phase-change random access memory
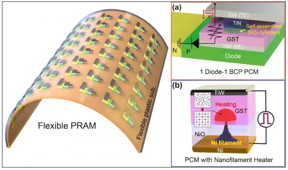 |
| Low-power nonvolatile PRAM for flexible and wearable memories enabled by (a) self-assembled BCP silica nanostructures and (b) self-structured conductive filament nanoheater. CREDIT: KAIST |
Abstract:
Phase change random access memory (PRAM) is one of the strongest candidates for next-generation nonvolatile memory for flexible and wearable electronics. In order to be used as a core memory for flexible devices, the most important issue is reducing high operating current. The effective solution is to decrease cell size in sub-micron region as in commercialized conventional PRAM. However, the scaling to nano-dimension on flexible substrates is extremely difficult due to soft nature and photolithographic limits on plastics, thus practical flexible PRAM has not been realized yet.
A KAIST research team develops the first flexible phase-change random access memory
Daejeon, Korea | Posted on June 15th, 2015Recently, a team led by Professors Keon Jae Lee and Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed the first flexible PRAM enabled by self-assembled block copolymer (BCP) silica nanostructures with an ultralow current operation (below one quarter of conventional PRAM without BCP) on plastic substrates. BCP is the mixture of two different polymer materials, which can easily create self-ordered arrays of sub-20 nm features through simple spin-coating and plasma treatments. BCP silica nanostructures successfully lowered the contact area by localizing the volume change of phase-change materials and thus resulted in significant power reduction. Furthermore, the ultrathin silicon-based diodes were integrated with phase-change memories (PCM) to suppress the inter-cell interference, which demonstrated random access capability for flexible and wearable electronics. Their work was published in the March issue of ACS Nano: "Flexible One Diode-One Phase Change Memory Array Enabled by Block Copolymer Self-Assembly."
Another way to achieve ultralow-powered PRAM is to utilize self-structured conductive filaments (CF) instead of the resistor-type conventional heater. The self-structured CF nanoheater originated from unipolar memristor can generate strong heat toward phase-change materials due to high current density through the nanofilament. This ground-breaking methodology shows that sub-10 nm filament heater, without using expensive and non-compatible nanolithography, achieved nanoscale switching volume of phase change materials, resulted in the PCM writing current of below 20 uA, the lowest value among top-down PCM devices. This achievement was published in the June online issue of ACS Nano "Self-Structured Conductive Filament Nanoheater for Chalcogenide Phase Transition." In addition, due to self-structured low-power technology compatible to plastics, the research team has recently succeeded in fabricating a flexible PRAM on wearable substrates.
Professor Lee said, "The demonstration of low power PRAM on plastics is one of the most important issues for next-generation wearable and flexible non-volatile memory. Our innovative and simple methodology represents the strong potential for commercializing flexible PRAM."
In addition, he wrote a review paper regarding the nanotechnology-based electronic devices in the June online issue of Advanced Materials entitled "Performance Enhancement of Electronic and Energy Devices via Block Copolymer Self-Assembly."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lan Yoon
82-102-539-4303
Copyright © Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() "Flexible One Diode-One Phase Change Memory Array Enabled by Block Copolymer Self-Assembly.":
"Flexible One Diode-One Phase Change Memory Array Enabled by Block Copolymer Self-Assembly.":
![]() "Self-Structured Conductive Filament Nanoheater for Chalcogenide Phase Transition.":
"Self-Structured Conductive Filament Nanoheater for Chalcogenide Phase Transition.":
![]() "Performance Enhancement of Electronic and Energy Devices via Block Copolymer Self-Assembly.":
"Performance Enhancement of Electronic and Energy Devices via Block Copolymer Self-Assembly.":
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








