Home > Press > New chip makes testing for antibiotic-resistant bacteria faster, easier: Researchers at the University of Toronto design diagnostic chip to reduce testing time from days to one hour, allowing doctors to pick the right antibiotic the first time
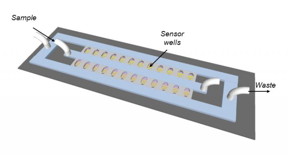 |
| Schematic of the antibiotic susceptibility testing device. The bacteria are cultured in miniature chambers, each of which contains a filter for bacterial capture and electrodes for readout of bacterial metabolism. CREDIT: U of T Engineering |
Abstract:
We live in fear of 'superbugs': infectious bacteria that don't respond to treatment by antibiotics, and can turn a routine hospital stay into a nightmare. A 2015 Health Canada report estimates that superbugs have already cost Canadians $1 billion, and are a "serious and growing issue." Each year two million people in the U.S. contract antibiotic-resistant infections, and at least 23,000 people die as a direct result.
New chip makes testing for antibiotic-resistant bacteria faster, easier: Researchers at the University of Toronto design diagnostic chip to reduce testing time from days to one hour, allowing doctors to pick the right antibiotic the first time
Toronto, Canada | Posted on May 28th, 2015But tests for antibiotic resistance can take up to three days to come back from the lab, hindering doctors' ability to treat bacterial infections quickly. Now Ph.D. researcher Justin Besant and his team at the University of Toronto have designed a small and simple chip to test for antibiotic resistance in just one hour, giving doctors a shot at picking the most effective antibiotic to treat potentially deadly infections. Their work was published this week in the international journal Lab on a Chip.
Resistant bacteria arise in part because of imprecise use of antibiotics -- when a patient comes down with an infection, the doctor wants to treat it as quickly as possible. Samples of the infectious bacteria are sent to the lab for testing, but results can take two to three days. In the meantime, the doctor prescribes her patient a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Sometimes the one-size-fits-all antibiotic works and sometimes it doesn't, and when the tests come back days later, the doctor can prescribe a specific antibiotic more likely to kill the bacteria.
"Guessing can lead to resistance to these broad-spectrum antibiotics, and in the case of serious infections, to much worse outcomes for the patient," says Besant. "We wanted to determine whether bacteria are susceptible to a particular antibiotic, on a timescale of hours, not days."
The problem with most current tests is the time it takes for bacteria to reproduce to detectable levels. Besant and his team, including his supervisor Professor Shana Kelley of the Institute for Biomaterials & Biomedical Engineering and the Faculties of Pharmacy and Medicine, and Professor Ted Sargent of The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, drew on their collective expertise in electrical and biomedical engineering to design a chip that concentrates bacteria in a miniscule space--just two nanolitres in volume--in order to increase the effective concentration of the starting sample.
They achieve this high concentration by 'flowing' the sample, containing the bacteria to be tested, through microfluidic wells patterned onto a glass chip. At the bottom of each well a filter, composed of a lattice of tiny microbeads, catches bacteria as the sample flows through. The bacteria accumulate in the nano-sized well, where they're trapped with the antibiotic and a signal molecule called resazurin.
Living bacteria metabolize resazurin into a form called resorufin, changing its electrochemical signature. If the bacteria are effectively killed by the antibiotic, they stop metabolizing resazurin and the electrochemical signature in the sample stays the same. If they are antibiotic-resistant, they continue to metabolize resazurin into resorufin, altering its electrochemical signature. Electrodes built directly into the chip detect the change in current as resazurin changes to resorcin.
"This gives us two advantages," says Besant. "One, we have a lot of bacteria in a very small space, so our effective starting concentration is much higher. And two, as the bacteria multiply and convert the resazurin molecule, it's effectively stuck in this nanolitre droplet--it can't diffuse away into the solution, so it can accumulate more rapidly to detectable levels."
"Our approach is the first to combine this method of increasing sample concentration with a straightforward electrochemical readout," says Professor Sargent. "We see this as an effective tool for faster diagnosis and treatment of commonplace bacterial infections."
Rapid alternatives to existing antibiotic resistance tests rely on fluorescence detection, requiring expensive and bulky fluorescence microscopes to see the result. "The electronics for our electrochemical readout can easily fit in a very small benchtop instrument, and this is something you could see in a doctor's office, for example," says Besant. "The next step would be to create a device that would allow you to test many different antibiotics at many different concentrations, but we're not there yet."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
RJ Taylor
416-978-4498
Copyright © University of Toronto
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Lab-on-a-chip
![]() Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
![]() Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








