Home > Press > Nano-policing pollution
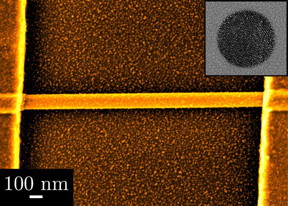 |
| Palladium nanoparticles were deposited on the entire wafer in an evenly distributed fashion, as seen in the background. They also attached on the surface of the copper oxide wire in the same evenly distributed manner, as seen in the foreground. On the upper right is a top view of a single palladium nanoparticle photographed with a transmission electron microscope(TEM) which can only produce black and white images. The nanoparticle is made up of columns consisting of palladium atoms stacked on top of each other. (This image has been modified from the original to provide a better visualization.) CREDIT: OIST |
Abstract:
Pollutants emitted by factories and car exhausts affect humans who breathe in these harmful gases and also aggravate climate change up in the atmosphere. Being able to detect such emissions is a critically needed measure.
Nano-policing pollution
Okinawa, Japan | Posted on May 13th, 2015New research by the Nanoparticles by Design Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST), in collaboration with the Materials Center Leoben Austria and the Austrian Centre for Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis has developed an efficient way to improve methods for detecting polluting emissions using a sensor at the nanoscale. The paper was published in Nanotechnology.
The researchers used a copper oxide nanowire decorated with palladium nanoparticles to detect carbon monoxide, a common industrial pollutant. The sensor was tested in conditions similar to ambient air since future devices developed from this method will need to operate in these conditions.
Copper oxide is a semiconductor and scientists use nanowires fabricated from it to search for potential application in the microelectronics industry. But in gas sensing applications, copper oxide was much less widely investigated compared to other metal oxide materials.
A semiconductor can be made to experience dramatic changes in its electrical properties when a small amount of foreign atoms are made to attach to its surface at high temperatures. In this case, the copper oxide nanowire was made part of an electric circuit. The researchers detected carbon monoxide indirectly, by measuring the change in the resulting circuit's electrical resistance in presence of the gas. They found that copper oxide nanowires decorated with palladium nanoparticles show a significantly greater increase in electrical resistance in the presence of carbon monoxide than the same type of nanowires without the nanoparticles.
The OIST Nanoparticles by Design Unit used a sophisticated technique that allowed them to first sift nanoparticles according to size, then deliver and deposit the palladium nanoparticles onto the surface of the nanowires in an evenly distributed manner. This even dispersion of size selected nanoparticles and the resulting nanoparticles-nanowire interactions are crucial to get an enhanced electrical response. The OIST nanoparticle deposition system can be tailored to deposit multiple types of nanoparticles at the same time, segregated on distinct areas of the wafer where the nanowire sits. In other words, this system can be engineered to be able to detect multiple kinds of gases. The next step is to detect different gases at the same time by using multiple sensor devices, with each device utilizing a different type of nanoparticle.
Compared to other options being explored in gas sensing which are bulky and difficult to miniaturize, nanowire gas sensors will be cheaper and potentially easier to mass produce.
The main energy cost in operating this kind of a sensor will be the high temperatures necessary to facilitate the chemical reactions for ensuring certain electrical response. In this study 350 degree centigrade was used. However, different nanowire-nanoparticle material configurations are currently being investigated in order to lower the operating temperature of this system.
"I think nanoparticle-decorated nanowires have a huge potential for practical applications as it is possible to incorporate this type of technology into industrial devices," said Stephan Steinhauer, a Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) postdoctoral research fellow working under the supervision of Prof. Mukhles Sowwan at the OIST Nanoparticles by Design Unit.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kaoru Natori
81-989-662-389
Copyright © Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate Univers
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








