Home > Press > Fast and accurate 3-D imaging technique to track optically trapped particles
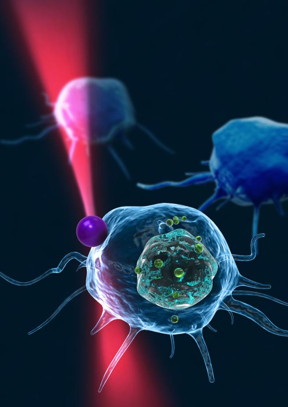 |
| This picture shows the concept image of tweezing an optically trapped glass bead on the cellular membrane of a white blood cell. CREDIT: KAIST |
Abstract:
KAIST researchers published an article on the development of a novel technique to precisely track the 3-D positions of optically trapped particles having complicated geometry in high speed in the April 2015 issue of Optica.
Fast and accurate 3-D imaging technique to track optically trapped particles
Daejeon, Korea | Posted on April 24th, 2015Optical tweezers have been used as an invaluable tool for exerting micro-scale force on microscopic particles and manipulating three-dimensional (3-D) positions of particles. Optical tweezers employ a tightly-focused laser whose beam diameter is smaller than one micrometer (1/100 of hair thickness), which generates attractive force on neighboring microscopic particles moving toward the beam focus. Controlling the positions of the beam focus enabled researchers to hold the particles and move them freely to other locations so they coined the name "optical tweezers."
To locate the optically-trapped particles by a laser beam, optical microscopes have usually been employed. Optical microscopes measure light signals scattered by the optically-trapped microscopic particles and the positions of the particles in two dimensions. However, it was difficult to quantify the particles' precise positions along the optic axis, the direction of the beam, from a single image, which is analogous to the difficulty of determining the front and rear positions of objects when closing an eye due to a lack of depth perception. Furthermore, it became more difficult to measure precisely 3-D positions of particles when scattered light signals were distorted by optically-trapped particles having complicated shapes or other particles occlude the target object along the optic axis.
Professor YongKeun Park and his research team in the Department of Physics at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) employed an optical diffraction tomography (ODT) technique to measure 3-D positions of optically-trapped particles in high speed. The principle of ODT is similar to X-ray CT imaging commonly used in hospitals for visualizing the internal organs of patients. Like X-ray CT imaging, which takes several images from various illumination angles, ODT measures 3-D images of optically-trapped particles by illuminating them with a laser beam in various incidence angles.
The KAIST team used optical tweezers to trap a glass bead with a diameter of 2 micrometers, and moved the bead toward a white blood cell having complicated internal structures. The team measured the 3-D dynamics of the white blood cell as it responded to an approaching glass bead via ODT in the high acquisition rate of 60 images per second. Since the white blood cell screens the glass bead along an optic axis, a conventionally-used optical microscope could not determine the 3-D positions of the glass bead. In contrast, the present method employing ODT localized the 3-D positions of the bead precisely as well as measured the composition of the internal materials of the bead and the white blood cell simultaneously.
Professor Park said, "Our technique has the advantage of measuring the 3-D positions and internal structures of optically-trapped particles in high speed without labelling exogenous fluorescent agents and can be applied in various fields including physics, optics, nanotechnology, and medical science."
Kyoohyun Kim, the lead author of this paper, added, "This ODT technique can also apply to cellular-level surgeries where optical tweezers are used to manipulate intracellular organelles and to display in real time and in 3-D the images of the reaction of the cell membrane and nucleus during the operation or monitoring the recovery process of the cells from the surgery."
The research results ("Simultaneous 3D Visualization and Position Tracking of Optically Trapped Particles Using Optical Diffraction Tomography") were published as the cover article in the April 2014 issue of Optica, the newest journal launched last year by the Optical Society of America (OSA) for rapid dissemination of high-impact results related to optics.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lan Yoon
82-423-502-294
Copyright © Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








