Home > Press > Better battery imaging paves way for renewable energy future
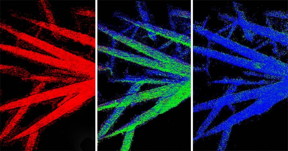 |
| Chemical phase map shows how the electrochemical discharge of iron fluoride microwires proceeded from 0 percent discharge (left), to 50 percent (middle), to 95 percent (right). CREDIT: Image provided by Linsen Li |
Abstract:
In a move that could improve the energy storage of everything from portable electronics to electric microgrids, University of Wisconsin-Madison and Brookhaven National Laboratory researchers have developed a novel X-ray imaging technique to visualize and study the electrochemical reactions in lithium-ion rechargeable batteries containing a new type of material, iron fluoride.
Better battery imaging paves way for renewable energy future
Madison, WI | Posted on April 20th, 2015"Iron fluoride has the potential to triple the amount of energy a conventional lithium-ion battery can store," says Song Jin, a UW-Madison professor of chemistry and Wisconsin Energy Institute affiliate. "However, we have yet to tap its true potential."
Graduate student Linsen Li worked with Jin and other collaborators to perform experiments with a state-of-the-art transmission X-ray microscope at the National Synchrotron Light Source at Brookhaven. There, they collected chemical maps from actual coin cell batteries filled with iron fluoride during battery cycling to determine how well they perform. The results are published today in the journal Nature Communications.
"In the past, we weren't able to truly understand what is happening to iron fluoride during battery reactions because other battery components were getting in the way of getting a precise image," says Li.
By accounting for the background signals that would otherwise confuse the image, Li was able to accurately visualize and measure, at the nanoscale, the chemical changes iron fluoride undergoes to store and discharge energy.
Thus far, using iron fluoride in rechargeable lithium ion batteries has presented scientists with two challenges. The first is that it doesn't recharge very well in its current form.
"This would be like your smart phone only charging half as much the first time, and even less thereafter," says Li. "Consumers would rather have a battery that charges consistently through hundreds of charges."
By examining iron fluoride transformation in batteries at the nanoscale, Jin and Li's new X-ray imaging method pinpoints each individual reaction to understand why capacity decay may be occurring.
"In analyzing the X-ray data on this level, we were able to track the electrochemical reactions with far more accuracy than previous methods, and determined that iron fluoride performs better when it has a porous microstructure," says Li.
The second challenge is that iron fluoride battery materials don't discharge as much energy as they take in, reducing energy efficiency. The current study yielded some preliminary insights into this problem and Jin and Li plan to tackle this challenge in future experiments.
Some implications of this research are obvious -- like using portable electronic devices for longer before charging -- but Jin also foresees a bigger and broader range of applications.
"If we can maximize the cycling performance and efficiency of these low-cost and abundant iron fluoride lithium ion battery materials, we could advance large-scale renewable energy storage technologies for electric cars and microgrids," he says.
Jin also believes that the novel X-ray imaging technique will facilitate the studies of other technologically important solid-state transformations and help to improve processes such as preparation of inorganic ceramics and thin-film solar cells.
###
The experiments were performed with the help of Yu-chen Karen Chen-Wiegart, Feng Wang, Jun Wang and their co-workers at Beamline X8C, National Synchrotron Light Source, Brookhaven National Laboratory, and supported by the U.S. Department of Energy Basic Energy Sciences and a seed grant from the Wisconsin Energy Institute. The synthesis of the battery materials in Jin's lab was supported by National Science Foundation Division of Materials Research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Song Jin
608-262-1562
Mark E. Griffin
608-890-2168
Copyright © University of Wisconsin-Madison
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








