Home > Press > Combined effort for structural determination
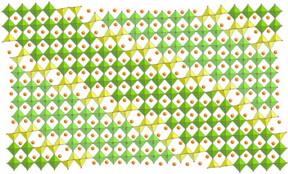 |
| This is the refined structure of (Pb,Bi)1 - xFe1 + xO3 - y. CREDIT: Batuk et al. |
Abstract:
Combining powder diffraction data with electron crystallography can give us a clearer view of modulated structures [Batuk et al. (2015). Acta Cryst. B71, 127-143; doi: 10.1107/S2052520615005466]
Combined effort for structural determination
Chester, UK | Posted on April 15th, 2015Electron crystallography has begun to be used routinely for solving otherwise intractable structures. When performed in an aberration-corrected microscope and combined with spectroscopic techniques, it can offer unprecedented detail down to sub-angstrom resolution. "The result of all this progress is that electron crystallography gives answers to more and more questions that used to be the domain of X-ray or neutron diffraction, and is especially useful when the X-ray or neutron experiment needs to be performed on a powder material, which limits the diffraction information available," explains Lukas Palatinus of the Czech Academy of Sciences in Prague in a commentary piece in Acta Crystallographica Section B [Palatinus (2015). Acta Cryst. B71, 125-126; doi: 10.1107/S2052520615005910].
Palatinus points out that when confronted with modulated structures, in which every atomic position is perturbed from one unit cell to the next by a modulation function, the construction of the structure model is much more complicated than for non-modulated materials. While effective techniques have been developed techniques to solve this problem from single crystal diffraction data, for powder diffraction data another approach to get around the problem is needed, which is where the work of Batuk and colleagues comes to the fore.
Batuk and colleagues have now shown how electron crystallography tools can be used to sidestep the limitations of powder diffraction and complement the structure analysis of modulated structures by powder diffraction. "The authors combine the results of their previous research with new results to provide an impressive overview of the available methods and information they can provide," explains Palatinus. The team investigated a series of anion-deficient perovskites to demonstrate proof of principle. In these materials, modulation arises as a consequence of the presence of crystallographic shear planes that have an average periodicity that is not in synchrony with the materials' basic periodicity.
Palatinus also points out that the choice of these materials was good for the given purpose. "These structures exhibit a wide variety of features that complicate the structure analysis of modulated structures from powder patterns," explains Palatinus. "It allowed the authors to illustrate many techniques and applications like the simultaneous imaging of heavy and light elements, atomic resolution chemical mapping or the mapping of the coordination number." Additionally, given the advent of perovskites in recent years as the focus of research into solar panel materials and other semiconductor applications new detailed information about their structures and properties are increasingly important.
"The local crystallographic information acquired using the scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM)-based methods in combination with the refinement from powder diffraction data can significantly improve the reliability of the crystal structure investigation," Batuk and colleagues report.
Of course, electron crystallography is very unlikely to make X-ray or neutron diffraction redundant any time soon, points out Palatinus, not least because a lot of materials are too short lived under the degrading eye of the electron beam. Moreover, electron techniques generally cannot be applied in situ in chemical reaction environments nor under pressure, instead requiring near vacuum conditions. Nevertheless, he adds that the team "shows convincingly how the electron crystallography methods have grown to a rich source of detailed information on the crystal structures, and it should convince any reader that resorting to these methods may very quickly solve problems that seem intractable by the more traditional approaches." It seems that as with many areas of study, a combined effort, the teamwork between different techniques that can complement each others, is needed to obtain the best results. "The key to success indeed lies in exploiting the complementarity and synergy between various methods," Palatinus says.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jonathan Agbenyega
44-124-434-2878
Copyright © International Union of Crystallography
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








