Home > Press > Harvesting energy from electromagnetic waves: In the future, clean alternatives such as harvesting energy from electromagnetic waves may help ease the world's energy shortage
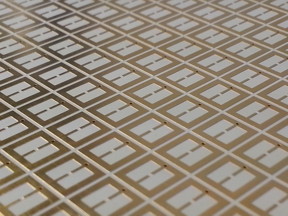 |
| The metasurface used for collecting electromagnetic energy is shown. CREDIT: O.Ramahi/U.Waterloo |
Abstract:
For our modern, technologically-advanced society, in which technology has become the solution to a myriad of challenges, energy is critical not only for growth but also, more importantly, survival. The sun is an abundant and practically infinite source of energy, so researchers around the world are racing to create novel approaches to "harvest" clean energy from the sun or transfer that energy to other sources.
Harvesting energy from electromagnetic waves: In the future, clean alternatives such as harvesting energy from electromagnetic waves may help ease the world's energy shortage
Washington, DC | Posted on April 15th, 2015This week in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Waterloo in Canada report a novel design for electromagnetic energy harvesting based on the "full absorption concept." This involves the use of metamaterials that can be tailored to produce media that neither reflects nor transmits any power--enabling full absorption of incident waves at a specific range of frequencies and polarizations.
"The growing demand for electrical energy around the globe is the main factor driving our research," said Thamer Almoneef, a Ph.D. student. "More than 80 percent of our energy today comes from burning fossil fuels, which is both harmful to our environment and unsustainable as well. In our group, we're trying to help solve the energy crisis by improving the efficiency of electromagnetic energy-harvesting systems."
Since the inception of collecting and harvesting electromagnetic energy, classical dipole patch antennas have been used. "Now, our technology introduces 'metasurfaces' that are much better energy collectors than classical antennas," explained Omar M. Ramahi, professor of electrical and computer engineering.
Metasurfaces are formed by etching the surface of a material with an elegant pattern of periodic shapes. The particular dimensions of these patterns and their proximity to each other can be tuned to provide "near-unity" energy absorption. This energy is then channeled to a load through a conducting path that connects the metasurface to a ground plane.
The key significance of the researchers' work is that it demonstrates for the first time that it's possible to collect essentially all of the electromagnetic energy that falls onto a surface.
"Conventional antennas can channel electromagnetic energy to a load--but at much lower energy absorption efficiency levels," said Ramahi. "We can also channel the absorbed energy into a load, rather than having the energy dissipate in the material as was done in previous works."
As you can imagine, this work has a broad range of applications. Among the most important is space solar power, an emerging critical technology that can significantly help to address energy shortages. It converts solar rays into microwaves--using conventional photovoltaic solar panels--and then beams the microwave's energy to microwave collector farms at designated locations on Earth. Japan is way out in front of rest of the world in this realm, with plans to begin harvesting solar power from space by 2030.
"Our research enables significantly higher energy absorption than classical antennas," Ramahi said. "This results in a significant reduction of the energy harvesting surface footprint. Real estate is a precious commodity for energy absorption--whether it's wind, hydro, solar or electromagnetic energy."
Other key applications include "wireless power transfer--directly adaptable to power remote devices such as RFID devices and tags or even remote devices in general," Ramahi noted.
The technology can also be extended to the infrared and visible spectra. "We've already extended our work into the infrared frequency regime and we hope to report very soon about near-unity absorption in those higher-frequency regimes," added Ramahi.
####
About American Institute of Physics
Applied Physics Letters features concise, rapid reports on significant new findings in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology. See: apl.aip.org
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
RFID
![]() Nanowire 'inks' enable paper-based printable electronics: Highly conductive films make functional circuits without adding high heat January 4th, 2017
Nanowire 'inks' enable paper-based printable electronics: Highly conductive films make functional circuits without adding high heat January 4th, 2017
![]() Conformal transfer of graphene for reproducible device fabrication August 11th, 2015
Conformal transfer of graphene for reproducible device fabrication August 11th, 2015
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








