Home > Press > Cooling massive objects to the quantum ground state
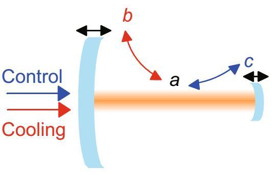 |
| This image shows an optomechanical system with two mechanical modes coupled to the same optical mode. CREDIT: ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Cooling of macroscopic and mesoscopic objects to the quantum ground states are of great interests not only for fundamental study of quantum theory but also for the broad applications in quantum information processing and high-precision metrology. However, the cooling limit is subjected to the quantum backaction, and ground state cooling is possible only in the resolved sideband limit, which requires the resonance frequency of the mechanical motion to be larger than the cavity decay rate. This sets a major obstacle for the ground state preparation and quantum manipulation of macroscopic and mesoscopic mechanical resonators, since more massive resonators typically have lower mechanical resonance frequencies. Therefore, it is essential to overcome this limitation, so that ground state cooling can be achieved for massive objects.
Cooling massive objects to the quantum ground state
Beijing, China | Posted on April 1st, 2015Very recently, Professor Yun-Feng Xiao and Ph.D student Yong-Chun Liu at Peking University, collaborated with Columbia University, have proposed an unresolved sideband ground-state cooling scheme in a generic optomechanical system, by taking advantage of the destructive quantum interference in a cavity optomechanical system with two mechanical modes coupled to the same optical cavity mode (Figure 1), where optomechanically-induced transparency phenomenon occurs. They find that using the multiple inputs, the cascaded cooling effect further suppresses the quantum backaction heating. They show that ground state cooling of the mechanical mode beyond the resolved sideband limit by nearly three orders of magnitude can be achieved.
"This cooling approach adds little complexity to the existing optomechanical system, which is crucial in the experimental point of view." said Yong-Chun Liu, the first author of the paper. Compared with the conventional backaction cooling approach, the additional requirement here is a control mechanical mode and one (or more) input laser. It is experimentally feasible for various optomechanical systems within current technical conditions. On one hand, many optomechanical systems possess abundant mechanical modes with different resonance frequencies, since the oscillation have different types and orders. This situation can be found in optomechanical systems using whispering-gallery microcavities, photonic crystal cavities, membranes, nanostrings and nanorods amongst others. On the other hand, composite optomechanical systems, containing two independent mechanical resonators, are also conceivable. For example, in Fabry-Perot cavities, the motion of one mirror acts as a control mechanical mode while the other mirror is to be cooled (Figure 1).
"This study paves the way for the manipulation of macroscopic mechanical resonators in the quantum regime." said Yun-Feng Xiao.
###
This research was funded by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant Nos. 2013CB328704 and 2013CB921904), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11474011, 11222440 and 61435001), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Grant No. 20120001110068) and the Optical Radiation Cooling and Heating in Integrated Devices Program of Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (Grant No. C11L10831).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yong-Chun Liu
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








