Home > Press > Graphene reduces wear of alumina ceramic
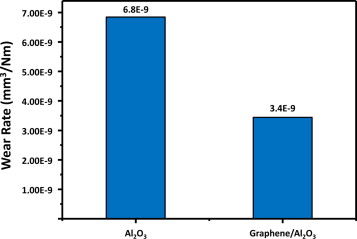 |
| The addition of graphene to alumina halves the wear rate copyright Elsevier |
Abstract:
Ceramics, hard crystalline solids, have been utilized by mankind for thousands of years, with earliest applications in pottery. In modern times, new ceramic materials were developed for use in advanced ceramic engineering, for example as semiconductors. One popular ceramic is alumina, an oxide of the metal aluminium.
Graphene reduces wear of alumina ceramic
San Sebastian, Spain | Posted on March 26th, 2015Alumina has for a long time been used in biomedical applications such as load-bearing hip prostheses and dental implants, due to its high resistance to corrosion, low friction, high wear resistance and strength. As material science progresses and advanced materials penetrate into society, ceramics are also continuously being improved, especially in strength and durability.
In a most recent development, Graphenea researchers, together with collaborators from Russia and throughout Spain, have shown that the addition of graphene to alumina improves the ceramic's wear resistance and decreases friction. The result is expected to soon find its use in real products, as graphene and its derivatives seem to be biocompatible and in addition carry a low cost.
The paper entitled "Wear behavior of graphene/alumina composite", published in the journal Ceramics International, describes the study of dry sliding behavior of a graphene/alumina composite material and compares it to regular alumina. The wear rate of the advanced composite was 50% lower than that of pure alumina, while the friction coefficient was reduced by 10%. This finding is made even more astonishing by the fact that the concentration of graphene in the final product is only 0.22% by weight. The type of graphene used for the study is Graphenea's standard graphene oxide.
Graphene-enhanced alumina has in itself not been studied much, and in fact there are few examples in literature of tribological studies of any graphene-enhanced ceramics. Graphenea's team recently participated in a study that showed that the addition of a small amount of graphene to alumina makes the ceramic less prone to breaking under strain, while simultaneously improving electrical conductivity.
The present experiment measured wear and friction by sliding the graphene/alumina composite material over a simulated distance of 10km. The material is slid in a "tribometer", a machine that simulates sliding behavior by bouncing a ceramic (in this case also alumina) ball off the tested material. The tribometer precisely measures the friction and wear as it goes. Such test instruments are often used to study novel hip implant designs. The testing of the material in this standard industrial tribometer puts the research close to end-user products.
####
About Graphenea
Graphenea, headquartered at the nanotechnology cluster CIC nanoGune in San Sebastian, Spain, was established in 2010, and has since grown to be one of the world's largest providers of graphene. Graphenea employs 12 people and exports graphene materials tomore than 370 customers in 53 countries. The company has focused on developing the CVD growth and transfer method, reaching a consistently high quality of its graphene films that researchers can rely on. Graphenea employs a team of skilled laboratory staff who have brought graphene transfer techniques to a new level, offering the same high quality films on any substrate. Following the trends in cutting-edge research, Graphenea also produces chemically exfoliated graphene, in volumes up to 2,5 litres per package. Graphenea partners with large multinationals to develop custom graphene materials for their applications.
Its research agility and ability to keep pace with the progress of graphene science and technology has allowed Graphenea to become the largest graphene supplier in the Graphene Flagship, a ten year project of the European Commission worth a billion euros. The company keeps a close relation with the world's leading scientists, regularly publishing scientific articles of the highest level.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Headquarters
Graphenea
Avenida de Tolosa, 76
20018 - Donostia/San Sebastián
Spain
Copyright © Graphenea
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Dental
![]() Innovations in dentistry: Navigational surgery, robotics, and nanotechnology October 2nd, 2020
Innovations in dentistry: Navigational surgery, robotics, and nanotechnology October 2nd, 2020
![]() First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
![]() Gas storage method could help next-generation clean energy vehicles: Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and methane can be stored in nanoscopic pores April 17th, 2020
Gas storage method could help next-generation clean energy vehicles: Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and methane can be stored in nanoscopic pores April 17th, 2020
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








