Home > Press > New Paper-like Material Could Boost Electric Vehicle Batteries: Researchers create silicon nanofibers 100 times thinner than human hair for potential applications in batteries for electric cars and personal electronics
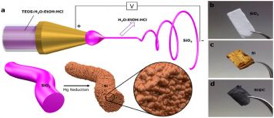 |
| (a) Schematic representation of the electrospinning process and subsequent reduction process. Digital photographs of (b) as-spun SiO2 nanofibers paper, (c) etched silicon nanofiber paper, and (d) carbon-coated silicon nanofiber paper as used in the lithium-ion half-cell configuration. |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of California, Riverside's Bourns College of Engineering have developed a novel paper-like material for lithium-ion batteries. It has the potential to boost by several times the specific energy, or amount of energy that can be delivered per unit weight of the battery.
New Paper-like Material Could Boost Electric Vehicle Batteries: Researchers create silicon nanofibers 100 times thinner than human hair for potential applications in batteries for electric cars and personal electronics
Riverside, CA | Posted on February 20th, 2015This paper-like material is composed of sponge-like silicon nanofibers more than 100 times thinner than human hair. It could be used in batteries for electric vehicles and personal electronics.
The findings were just published in a paper, "Towards Scalable Binderless Electrodes: Carbon Coated Silicon Nanofiber Paper via Mg Reduction of Electrospun SiO2 Nanofibers," in the journal Nature Scientific Reports. The authors were Mihri Ozkan, a professor of electrical and computer engineering, Cengiz S. Ozkan, a professor of mechanical engineering, and six of their graduate students: Zach Favors, Hamed Hosseini Bay, Zafer Mutlu, Kazi Ahmed, Robert Ionescu and Rachel Ye.
The nanofibers were produced using a technique known as electrospinning, whereby 20,000 to 40,000 volts are applied between a rotating drum and a nozzle, which emits a solution composed mainly of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), a chemical compound frequently used in the semiconductor industry. The nanofibers are then exposed to magnesium vapor to produce the sponge-like silicon fiber structure.
Conventionally produced lithium-ion battery anodes are made using copper foil coated with a mixture of graphite, a conductive additive, and a polymer binder. But, because the performance of graphite has been nearly tapped out, researchers are experimenting with other materials, such as silicon, which has a specific capacity, or electrical charge per unit weight of the battery, nearly 10 times higher than graphite.
The problem with silicon is that is suffers from significant volume expansion, which can quickly degrade the battery. The silicon nanofiber structure created in the Ozkan's labs circumvents this issue and allows the battery to be cycled hundreds of times without significant degradation.
"Eliminating the need for metal current collectors and inactive polymer binders while switching to an energy dense material such as silicon will significantly boost the range capabilities of electric vehicles," Favors said.
This technology also solves a problem that has plagued free-standing, or binderless, electrodes for years: scalability. Free-standing materials grown using chemical vapor deposition, such as carbon nanotubes or silicon nanowires, can only be produced in very small quantities (micrograms). However, Favors was able to produce several grams of silicon nanofibers at a time even at the lab scale.
The researchers' future work involves implementing the silicon nanofibers into a pouch cell format lithium-ion battery, which is a larger scale battery format that can be used in EVs and portable electronics.
The research is supported by Temiz Energy Technologies. The UC Riverside Office of Technology Commercialization has filed patents for inventions reported in the research paper.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sean Nealon
Tel: (951) 827-1287
Twitter: seannealon
ADDITIONAL CONTACTS
Cengiz Ozkan
Tel: 951-827-5016
Mihri Ozkan
Tel: 951-827-2900
Copyright © University of California - Riverside
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Patents/IP/Tech Transfer/Licensing
![]() Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
![]() Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








