Home > Press > Visualizing interacting electrons in a molecule: Scientists at Aalto University and the University of Zurich have succeeded in directly imaging how electrons interact within a single molecule
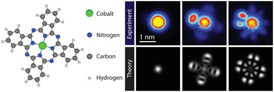 |
| The image on left shows: Chemical structure of cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPC). The image on right shows: Experimental and theoretical wave functions of CoPC.
CREDIT: Aalto University |
Abstract:
Understanding this kind of electronic effects in organic molecules is crucial for their use in optoelectronic applications, for example in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) and solar cells.
Visualizing interacting electrons in a molecule: Scientists at Aalto University and the University of Zurich have succeeded in directly imaging how electrons interact within a single molecule
Aalto, Finland | Posted on January 26th, 2015In their article published in Nature Physics, the research team demonstrates measurements on the organic molecule cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPC) that can be explained only by taking into consideration how electrons in the molecule interact with each other. CoPC is a commonly used molecule in organic optoelectronic devices. Electron-electron interactions alter its conductivity, which is directly related to device performance.
The Atomic Scale Physics group at Aalto University headed by Peter Liljeroth specializes on scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), which utilizes a tiny current between a sharp probe tip and a conducting sample to measure structural and electronic properties of the sample surface with atomic resolution. In this case, they used the STM to measure the current passing through a single molecule on a surface by injecting or removing electrons at different energies.
Within the molecule, electrons 'live' on so-called orbitals, which define their energy and the shape of their quantum mechanical wavefunction. These orbitals can be measured by recording the current through the molecule as a function of the applied voltage.
Fabian Schulz, a post-graduate researcher in Liljeroth's group, was surprised when the measurements on CoPC molecules did not fit the conventional interpretation of STM experiments on single molecules. "We saw several additional features in the recorded current where there should have been none according to the usual interpretation of these so-called tunneling spectra", Schulz explains.
The experiments were performed on cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPC) molecules deposited on a one-atom thick layer of hexagonal boron nitride on an iridium surface.
A colleague from Aalto University and leader of the Quantum Many-Body Physics group, Ari Harju, suggested that the key to understanding the experimental results might be a form of electron-electron interaction that usually is neglected in interpreting such experiments. In collaboration with Ari P. Seitsonen from the University of Zurich, Ari Harju and his team calculated the electronic properties of the molecule, including quantum mechanical effects that went beyond prevailing methods. This novel interpretation was confirmed when Liljeroth and his team were able to match the experimentally measured molecular orbitals with the predictions of the theory. "It was very exciting to see this kind of an interplay between theory and experiment", Liljeroth remarks.
Ari Harju concludes: "The proof that such theoretically predicted, exotic effects can be observed experimentally is an important step forward in understanding how current is transported across individual molecules and molecular assemblies."
###
The study was performed at Aalto University Department of Applied Physics and at the University of Zurich. The groups at Aalto are part of the Academy of Finland's Centres of Excellence in "Low Temperature Quantum Phenomena and Devices" and "Computational Nanosciences". Academy of Finland and the European Research Council ERC funded the research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Peter Liljeroth
358-503-636-115
Copyright © Aalto University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








