Home > Press > Studies on exotic superfluids in spin-orbit coupled Fermi gases were reviewed
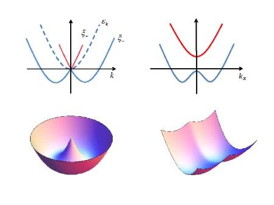 |
| Schematic illustration of the single-particle spectra modified by spin-orbit coupling. The Rashba-type spin-orbit coupling can lead to a degenerate ring in momentum space for the lower branch of the single-particle dispersion spectra (left). The lower-branch dispersion spectrum under the NIST-type spin-orbit coupling (right) is less symmetric. These differences, as well as the hyperfine-spin dependence of the single-particle dispersion under spin-orbit coupling, give rise to rich physics in these systems. ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Ultracold atomic gases have been widely considered as ideal platforms for quantum simulation. Thanks to the clean environment and the highly tunable parameters in these systems, many interesting physical models can be simulated using cold atomic gases, and various novel many-body states have been prepared and probed experimentally. The recent experimental realization of synthetic gauge field in ultracold atomic gases has significantly extended the horizon of quantum simulation with cold atoms. As a special form of synthetic gauge field, synthetic spin-orbit coupling has attracted much attention recently. Professor YI Wei from University of Science and Technology of China, Professor ZHANG Wei from Renmin University of China, and Professor CUI Xiaoling from Chinese Academy of Sciences reviewed the recent theoretical studies on various novel pairing superfluid phases in spin-orbit coupled ultracold Fermi gases. They showed that spin-orbit coupling modifies the single-particle spectra, which gives rise to exotic few-body correlations and interesting pairing states. The review article, entitled "Pairing superfluidity in spin-orbit coupled ultracold Fermi gases", was published in SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2015, Vol. 58(1).
Studies on exotic superfluids in spin-orbit coupled Fermi gases were reviewed
Beijing, China | Posted on December 30th, 2014In condensed-matter materials, spin-orbit coupling plays a key role in many interesting phenomena, such as quantum spin Hall effects, topological insulators, and topological superconductors. With the availability of synthetic spin-orbit coupling as a tool of quantum control, people hope to simulate various topological phases, the topological superfluid state in particular, in the highly controllable environment of ultracold Fermi gases. Indeed, recent theoretical studies have suggested that exotic superfluid phases and novel phenomena can be engineered with carefully designed configurations. By reviewing these theoretical studies, YI et al. discuss the exotic superfluid phases in systems with different spatial dimensions and with different forms of spin-orbit coupling. A fundamentally important effect of spin-orbit coupling is the modification of single-particle dispersion spectra. The review focuses on how this effect leads to interesting pairing phases such as the topological superfluid state, various gapless superfluid states, the spin-orbit-coupling-induced Fulde-Ferrell state, and the topological Fulde-Ferrell state. Besides many-body physics, the change in the single-particle dispersion can also induce novel few-body correlations, for example, a three-body bound state in the absence of any stable two-body bound state. These interesting few-body states, if observed, should no doubt give rise to even more exotic many-body properties.
###
By reviewing these topics, the article summarizes the latest developments in the theoretical study of pairing physics in spin-orbit coupled Fermi gases, and is helpful for future theoretical and experimental characterization of the rich physics in these systems. The research project was partially supported by grants from the National Key Basic Research Program, the National Fundamental Research Program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the Research Funds of Renmin University, and the programs of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
YI Wei
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








