Home > Press > Atmospheric carbon dioxide used for energy storage products
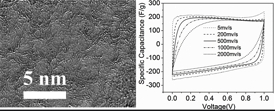 |
| Nanoporous graphene |
Abstract:
Researchers have discovered a fascinating new way to take some of the atmospheric carbon dioxide that's causing the greenhouse effect and use it to make an advanced, high-value material for use in energy storage products.
Atmospheric carbon dioxide used for energy storage products
Corvallis, OR | Posted on December 2nd, 2014Chemists and engineers at Oregon State University have discovered a fascinating new way to take some of the atmospheric carbon dioxide that's causing the greenhouse effect and use it to make an advanced, high-value material for use in energy storage products.
This innovation in nanotechnology won't soak up enough carbon to solve global warming, researchers say. However, it will provide an environmentally friendly, low-cost way to make nanoporous graphene for use in "supercapacitors" - devices that can store energy and release it rapidly.
Such devices are used in everything from heavy industry to consumer electronics.
The findings were just published in Nano Energy by scientists from the OSU College of Science, OSU College of Engineering, Argonne National Laboratory, the University of South Florida and the National Energy Technology Laboratory in Albany, Ore. The work was supported by OSU.
In the chemical reaction that was developed, the end result is nanoporous graphene, a form of carbon that's ordered in its atomic and crystalline structure. It has an enormous specific surface area of about 1,900 square meters per gram of material. Because of that, it has an electrical conductivity at least 10 times higher than the activated carbon now used to make commercial supercapacitors.
"There are other ways to fabricate nanoporous graphene, but this approach is faster, has little environmental impact and costs less," said Xiulei (David) Ji, an OSU assistant professor of chemistry in the OSU College of Science and lead author on the study. "The product exhibits high surface area, great conductivity and, most importantly, it has a fairly high density that is comparable to the commercial activated carbons.
"And the carbon source is carbon dioxide, which is a sustainable resource, to say the least," Ji said. "This methodology uses abundant carbon dioxide while making energy storage products of significant value."
Because the materials involved are inexpensive and the fabrication is simple, this approach has the potential to be scaled up for production at commercial levels, Ji said.
The chemical reaction outlined in this study involved a mixture of magnesium and zinc metals, a combination discovered for the first time. These are heated to a high temperature in the presence of a flow of carbon dioxide to produce a controlled "metallothermic" reaction. The reaction converted the elements into their metal oxides and nanoporous graphene, a pure form of carbon that's remarkably strong and can efficiently conduct heat and electricity. The metal oxides could later be recycled back into their metallic forms to make an industrial process more efficient.
By comparison, other methods to make nanoporous graphene often use corrosive and toxic chemicals, in systems that would be challenging to use at large commercial levels.
"Most commercial carbon supercapacitors now use activated carbon as electrodes, but their electrical conductivity is very low," Ji said. "We want fast energy storage and release that will deliver more power, and for that purpose the more conductive nanoporous graphene will work much better. This solves a major problem in creating more powerful supercapacitors."
A supercapacitor is a type of energy storage device, but it can be recharged much faster than a battery and has a great deal more power. They are mostly used in any type of device where rapid power storage and short, but powerful energy release is needed.
They are being used in consumer electronics, and have applications in heavy industry, with the ability to power anything from a crane to a forklift. A supercapacitor can capture energy that might otherwise be wasted, such as in braking operations. And their energy storage abilities may help "smooth out" the power flow from alternative energy systems, such as wind energy.
They can power a defibrillator, open the emergency slides on an aircraft and greatly improve the efficiency of hybrid electric automobiles. Nanoporous carbon materials can also adsorb gas pollutants, work as environmental filters, or be used in water treatment. The uses are expanding constantly and have been constrained mostly by their cost.
####
About Oregon State University
OSU is one of only two U.S. universities designated a land-, sea-, space- and sun-grant institution. OSU is also Oregon’s only university to hold both the Carnegie Foundation’s top designation for research institutions and its prestigious Community Engagement classification. Its more than 26,000 students come from all 50 states and more than 90 nations. OSU programs touch every county within Oregon, and its faculty teach and conduct research on issues of national and global importance.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Xiulei (David) Ji
541-737-6798
Copyright © Oregon State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








