Home > Press > A billion holes can make a battery
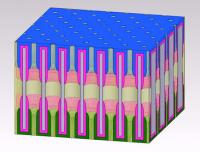 |
| A billion nanopores could fit on a postage stamp.
Credit: NEES, a DOE Energy Frontier Research Center |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of Maryland have invented a single tiny structure that includes all the components of a battery that they say could bring about the ultimate miniaturization of energy storage components.
Engineers at the University of Maryland have invented a single tiny structure that includes all the components of a battery that they say could bring about the ultimate miniaturization of energy storage.
A billion holes can make a battery
College Park, MD | Posted on November 10th, 2014The structure is called a nanopore: a tiny hole in a ceramic sheet that holds electrolyte to carry the electrical charge between nanotube electrodes at either end. The existing device is a test, but the bitsy battery performs well. First author Chanyuan Liu, a graduate student in materials science & engineering, says that it can be fully charged in 12 minutes, and it can be recharged thousands of time.
A team of UMD chemists and materials scientists collaborated on the project: Gary Rubloff , director of the Maryland NanoCenter and a professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and in the Institute for Systems Research; Sang Bok Lee, a professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemisty and the Department of Materials Science and Engineering; and seven of their Ph.D. students (two now graduated).
Many millions of these nanopores can be crammed into one larger battery the size of a postage stamp. One of the reasons the researchers think this unit is so successful is because each nanopore is shaped just like the others, which allows them to pack the tiny thin batteries together efficiently. Coauthor Eleanor Gillette's modeling shows that the unique design of the nanopore battery is responsible for its success.
The space inside the holes is so small that the space they take up, all added together, would be no more than a grain of sand.
Now that the scientists have the battery working and have demonstrated the concept, they have also identified improvements that could make the next version 10 times more powerful. The next step to commercialization: the inventors have conceived strategies for manufacturing the battery in large batches.
The research was funded by the Department of Energy. It will be published on November 10 in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
"An all-in-one nanopore battery array," Nature Nanotechnology (2014), Chanyuan Liu, Eleanor I. Gillette, Xinyi Chen, Alexander J. Pearse, Alexander C. Kozen, Marshall A. Schroeder, Keith E. Gregorczyk, Sang Bok Lee and Gary W. Rubloff
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Martha Heil
301-405-0876
Copyright © University of Maryland
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








