Home > Press > Unique catalysts for hydrogen fuel cells synthesized in ordinary kitchen microwave oven
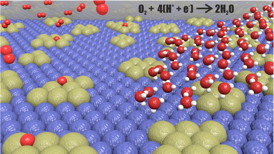 |
| A schematic model of the unique morphology of the alloy. The Pd-islands (light-brown spheres) are embedded in an environment of tungsten (blue spheres). Oxygen are represented by red spheres, and hydrogen by white spheres. |
Abstract:
Swedish and Chinese researchers show how a unique nano-alloy composed of palladium nano-islands embedded in tungsten nanoparticles creates a new type of catalysts for highly efficient oxygen reduction, the most important reaction in hydrogen fuel cells. Their results are published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Unique catalysts for hydrogen fuel cells synthesized in ordinary kitchen microwave oven
Umea, Sweden | Posted on October 14th, 2014The world's rapidly growing demand for energy and the requirement of sustainable energy production calls for an urgent change in today's fossil fuel based energy system. Research groups worldwide work intensively to develop novel advanced energy conversion and storage systems with high efficiency, low cost and environmental compatibility.
Fuel cell systems represent a promising alternative for low carbon emission energy production. Traditional fuel cells are however limited by the need of efficient catalysts to drive the chemical reactions involved in the fuel cell. Historically, platinum and its alloys have frequently been used as anodic and cathodic catalysts in fuel cells, but the high cost of platinum, due to its low abundance, motivates researchers to find efficient catalysts based on earth-abundant elements.
"In our study we report a unique novel alloy with a palladium (Pd) and tungsten (W) ratio of only one to eight, which still has similar efficiency as a pure platinum catalyst. Considering the cost, it would be 40 times lower", says Thomas Wågberg, Senior lecturer at Department of Physics, Umeå University.
The explanation for the very high efficiency is the unique morphology of the alloy. It is neither a homogeneous alloy, nor a fully segregated two-phase system, but rather something in between.
By advanced experimental and theoretical investigations, the researchers show that the alloy is composed of metallic Pd-islands embedded in the Pd-W alloy. The size of the islands are about one nanometer in diameter and are composed of 10-20 atoms that are segregated to the surface. The unique environment around the Pd-islands give rise to special effects that all together turn the islands into highly efficient catalytic hot-spots for oxygen reduction.
To stabilize the nanoparticles in practical applications, they are anchored on ordered mesoporous carbon. The anchoring keep the nanoparticles stable over long time by hindering them from fusing together in the fuel cell tests.
"The unique formation of the material is based on a synthesis method, which can be performed in an ordinary kitchen micro-wave oven purchased at the local supermarket. If we were not using argon as protective inert gas, it would be fully possible to synthesize this advanced catalyst in my own kitchen! ", says Thomas Wågberg.
Wågberg and his fellow researchers have recently received funding from the Kempe Foundation to buy a more advanced micro-wave oven, and therefore they will be able to run more advanced experiments to fine tune some of the catalyst properties.
The Artificial Leaf
The study has been conducted within the artificial leaf project, which is funded by Knut and Alice Wallenberg foundation. Physicist, chemists, and plant science researchers at Umeå University work together in the search for clean and renewable energy sources.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Thomas Wågberg
46-072-715-5993
Copyright © Umea University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








