Home > Press > Tailored flexible illusion coatings hide objects from detection
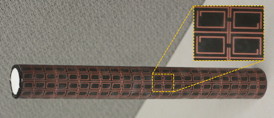 |
| Antenna covered with copper patterned dielectric substrate creates a flexible metasurface that acts as an illusion coating, cloaking the antenna or making it appear to be something entirely different. Image: Zhihao Jiang/Penn State |
Abstract:
Developing the cloak of invisibility would be wonderful, but sometimes simply making an object appear to be something else will do the trick, according to Penn State electrical engineers.
Tailored flexible illusion coatings hide objects from detection
University Park, PA | Posted on October 13th, 2014"Previous attempts at cloaking using a single metasurface layer were restricted to very small-sized objects," said Zhi Hao Jiang, postdoctoral fellow in electrical engineering, Penn State. "Also, the act of cloaking would prevent an enclosed antenna or sensor from communicating with the outside world."
Jiang and Douglas H. Werner, John L. and Genevieve H. McCain Chair Professor of Electrical Engineering, developed a metamaterial coating with a negligible thickness that allows coated objects to function normally while appearing as something other than what they really are, or even completely disappearing. They report their research in Advanced Functional Materials.
The researchers employ what they call "illusion coatings," coatings made up of a thin flexible substrate with copper patterns designed to create the desired result. They can take a practical size metal antenna or sensor, coat it with the patterned film and when the device is probed by a radio frequency source, the scattering signature of the enclosed object will appear to be that of a prescribed dielectric material like silicon or Teflon. Conversely, with the proper pattern, they can coat a dielectric and it will scatter electromagnetic waves the same as if it were a metal object.
"The demonstrated illusion/cloaking coating is a lightweight two-dimensional metasurface, not a bulky three-dimensional metasurface," said Werner.
The researchers take the object they want cloaked and surround it with a spacer, either air or foam. They then apply the ultrathin layer of dielectric with copper patterning designed for the wavelengths they wish to cloak. In this way, antennae and sensors could be made invisible or deceptive to remote inspection.
Another application of this material would be to protect objects from other emitting objects nearby while still allowing electromagnetic communication between them. This was not possible with the conventional transformation optics-based cloaking method because the cloaking mechanism electromagnetically blocked the cloaked object from the outside, but this new coating allows the object surrounded to continue working while being protected. In an array of antennae, for example, interference from the nearby antennas can be suppressed.
The metasurface coating consists of a series of copper, geometric patterns placed on a flexible substrate using standard lithographic methods currently used to create printed circuit boards. Each illusion coating must be designed for the specific application, but the designs are optimized mathematically. This method of manufacture is low cost and well established.
Another advantage of this method is that it works not only for direct hits by radio frequency waves incident normally on the coated object, but also continues to operate properly within a 20 degree field of view, making it a better angle-tolerant shield than previous attempts that employed bulky metamaterials. Currently, the metasurface coatings only work on narrow bands of the spectrum for any application, but can be adapted to work in other bands of the electromagnetic spectrum including the visible spectrum.
"We haven't tried expanding the bandwidth yet," said Werner. "But the theory suggests that it should be possible and it will probably require multiple layers with different patterns to do that."
Illusion coatings could be used for things other than hiding. They could enhance the way radio frequency ID tags work or could redistribute energy in different, controlled patterns making things more visible rather than less visible. The materials shielding ability can also be used to protect any type of equipment from stray or intentional electromagnetic interference.
###
The National Science Foundation supported this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
814-865-9481
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








