Home > Press > Diamond defect interior design: Planting imperfections called 'NV centers' at specific spots within a diamond lattice could advance quantum computing and atomic-scale measurement
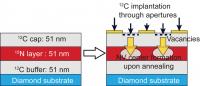 |
| This is a schematic of the process to localize NV centers in 3-D. The researchers blasted carbon ions through holes to create vacancies and heated the diamond to make the vacancies mobile within the crystal. NV centers could form in the nitrogen-doped layer below where the holes were placed.
Credit: F.J. Heremans and D. Awschalom/U. Chicago and K. Ohno/UCSB |
Abstract:
By carefully controlling the position of an atomic-scale diamond defect within a volume smaller than what some viruses would fill, researchers have cleared a path toward better quantum computers and nanoscale sensors. They describe their technique in a paper published in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
Diamond defect interior design: Planting imperfections called 'NV centers' at specific spots within a diamond lattice could advance quantum computing and atomic-scale measurement
Washington, DC | Posted on August 5th, 2014David Awschalom, a physicist at the Institute for Molecular Engineering at the University of Chicago, and his colleagues study a technologically useful diamond defect called a nitrogen vacancy (NV) center. NV centers consist of a nitrogen atom adjacent to a vacant spot that replaces two carbon atoms in the diamond crystal, leaving an unpaired electron. Researchers can use a property of the unpaired electron known as its spin to store and transmit quantum information at room temperature.
Qubits and Quantum Sensors
NV centers are attractive candidates for qubits, the quantum equivalent of a classical computing bit. A single NV center can also be used for completely different applications, such as measuring temperature, as well as to image electric and magnetic fields on the nanometer-scale by placing it at the tip of a diamond-based scanning probe.
A primary obstacle to further exploiting NV centers for practical quantum computing and nanoscale sensing devices lies in the difficulty of placing the centers within what Awschalom calls the functional "sweet spots" of the devices. Another challenge is increasing the NV center density without sacrificing their spin lifetimes, which must remain long in order to extract the most useful information from the system.
Awschalom and his colleagues have developed a new way to create NV centers that could help overcome both these challenges.
That's the Spot
The key to the team's new approach is to create the nitrogen and vacancy defects separately, Awschalom said. First, the team grew a layer of nitrogen-doped crystal within a diamond film. The researchers kept the nitrogen layer extremely thin by reducing the growth rate of the film to approximately 8 nanometers/hour. The nanometer-scale nitrogen-doped layer constrains the possible location of the NV centers in the depth direction.
Secondly, the researchers created a mask to cover the film, leaving only pinprick holes. They blasted carbon ions through the holes to create vacancies and heated the diamond to make the vacancies mobile within the crystal. NV centers could form in the nitrogen-doped layer below where the holes were placed.
Using this approach the team successfully localized NV centers within a cavity approximately 180 nanometers across -- a volume small enough to be compatible with many diamond-based nanostructures used in sensing devices and experimental quantum information systems.
The localized NV centers could also hold a specific spin for longer than 300 microseconds. This so-called spin coherence time was an order of magnitude better than that achieved by other 3-D localization methods. The longer spin lifetime means the NV centers can detect smaller magnetic signals and hold quantum information for longer.
One of the team's goals for using their new technique is to measure the nuclear spins of hydrogen atoms - one of the tiniest magnetic signals - within a biological molecule. The research could reveal new insights into how important biological functions like photosynthesis work. "Our research impacts diverse fields of science and technology," Awschalom said. "Technological advancements always open new avenues of scientific research."
The authors of this paper are affiliated with the University of California, Santa Barbara and the University of Chicago.
####
About American Institute of Physics (AIP)
Applied Physics Letters features concise, rapid reports on significant new findings in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Alliances/Trade associations/Partnerships/Distributorships
![]() Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








