Home > Press > A new way to make microstructured surfaces: Method can produce strong, lightweight materials with specific surface properties
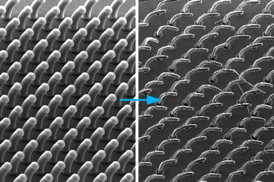 |
| New process developed by MIT’s John Hart and others can produce arrays of 3-D shapes, based on carbon nanotubes growing from a surface. In this example, all the nanotubes are aligned to curve in the same direction.
Illustration courtesy of the researchers |
Abstract:
A team of researchers has created a new way of manufacturing microstructured surfaces that have novel three-dimensional textures. These surfaces, made by self-assembly of carbon nanotubes, could exhibit a variety of useful properties — including controllable mechanical stiffness and strength, or the ability to repel water in a certain direction.
A new way to make microstructured surfaces: Method can produce strong, lightweight materials with specific surface properties
Cambridge, MA | Posted on July 29th, 2014"We have demonstrated that mechanical forces can be used to direct nanostructures to form complex three-dimensional microstructures, and that we can independently control … the mechanical properties of the microstructures," says A. John Hart, the Mitsui Career Development Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering at MIT and senior author of a paper describing the new technique in the journal Nature Communications.
The technique works by inducing carbon nanotubes to bend as they grow. The mechanism is analogous to the bending of a bimetallic strip, used as the control in old thermostats, as it warms: One material expands faster than another bonded to it. But in this new process, the material bends as it is produced by a chemical reaction.
The process begins by printing two patterns onto a substrate: One is a catalyst of carbon nanotubes; the second material modifies the growth rate of the nanotubes. By offsetting the two patterns, the researchers showed that the nanotubes bend into predictable shapes as they extend.
"We can specify these simple two-dimensional instructions, and cause the nanotubes to form complex shapes in three dimensions," says Hart. Where nanotubes growing at different rates are adjacent, "they push and pull on each other," producing more complex forms, Hart explains. "It's a new principle of using mechanics to control the growth of a nanostructured material," he says.
Few high-throughput manufacturing processes can achieve such flexibility in creating three-dimensional structures, Hart says. This technique, he adds, is attractive because it can be used to create large expanses of the structures simultaneously; the shape of each structure can be specified by designing the starting pattern. Hart says the technique could also enable control of other properties, such as electrical and thermal conductivity and chemical reactivity, by attaching various coatings to the carbon nanotubes after they grow.
"If you coat the structures after the growth process, you can exquisitely modify their properties," says Hart. For example, coating the nanotubes with ceramic, using a method called atomic layer deposition, allows the mechanical properties of the structures to be controlled. "When a thick coating is deposited, we have a surface with exceptional stiffness, strength, and toughness relative to [its] density," Hart explains. "When a thin coating is deposited, the structures are very flexible and resilient."
This approach may also enable "high-fidelity replication of the intricate structures found on the skins of certain plants and animals," Hart says, and could make it possible to mass-produce surfaces with specialized characteristics, such as the water-repellent and adhesive ability of some insects. "We're interested in controlling these fundamental properties using scalable manufacturing techniques," Hart says.
Hart says the surfaces have the durability of carbon nanotubes, which could allow them to survive in harsh environments, and could be connected to electronics and function as sensors of mechanical or chemical signals.
Along with Hart, the research team included Michael de Volder of Cambridge University; Sei Jin Park, a visiting doctoral student from the University of Michigan; and Sameh Tawfick, a former postdoc at MIT who is now at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The work was supported by the European Research Council, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
Written by David L. Chandler, MIT News Office
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Abby Abazorius
MIT News Office
617.253.2709
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Faculty Highlight: A. John Hart
Faculty Highlight: A. John Hart
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








