Home > Press > Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM
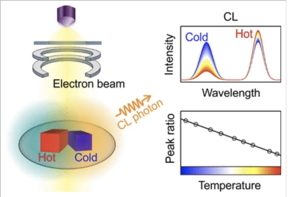 |
| Schematic illustration of the cathodoluminescence (CL) nanothermometry. CREDIT UNIST |
Abstract:
A groundbreaking method for measuring the temperature of nanometer-sized samples within a transmission electron microscope (TEM) has been developed by Professor Oh-Hoon Kwon and his research team in the Department of Chemistry at UNIST. This innovative technology, utilizing nano-thermometers based on cathodoluminescence (CL) spectroscopy, opens up new possibilities for analyzing the thermodynamic properties of fine samples and advancing the development of high-tech materials.
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM
Ulsan, South Korea | Posted on March 8th, 2024The transmission electron microscope allows researchers to observe samples at a magnification of hundreds of thousands of times by transmitting a short-wavelength electron beam through the sample. By detecting light emitted from the sample through cathode ray emission spectroscopy, researchers can finely analyze the physical and optical properties of the sample at nanometer scales.
The newly developed nano-thermometers rely on the temperature-dependent intensity variation of a specific cathode ray emission band of europium ions (Eu3+). By synthesizing nanoparticles doped with europium ions within gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3), the research team ensured minimal damage from the electron beam, enabling long-term experiments.
Through dynamic analysis, the team confirmed that the intensity ratio of the light emitting band from europium ions is a reliable indicator of temperature, with an impressive measurement error of about 4℃ using nano thermometer particles measuring approximately 100 nanometers in size. This method offers more than twice the accuracy of conventional TEM temperature measurement techniques and significantly improves spatial resolution.
Furthermore, the team demonstrated the applicability of the nano-thermometers by inducing temperature changes with a laser within the TEM and simultaneously measuring temperature and structural variations in real-time. This capability allows for the analysis of thermodynamic properties at the nanometer level in response to external stimuli, without interfering with standard TEM analysis procedures.
Won-Woo Park, the first author of the study, emphasized the non-invasive nature of the temperature measurement process, highlighting that the interaction between the transmission electron beam and the nano-thermometer particles enables real-time temperature detection without disrupting TEM imaging. He noted, “The big advantage of the developed nanometer is that the temperature measurement process does not interfere with the existing transmission electron microscope analysis,” adding, “Since temperature is measured using light, a by-product generated by the interaction between the transmission electron beam and the nanometer particle, it is possible to measure the image of the transmission electron microscope and detect the temperature in real time.”
Professor Kwon underscored the significance of this research, stating that “The developed temperature measurement indicators, when combined with real-time imaging techniques, facilitate the observation of local temperature changes in response to external stimuli.” He further stated, “This advancement is poised to significantly contribute to the development of high-tech materials such as secondary batteries and displays.”
The findings of this research have been published in the online version of ACS Nano on January 30, 2024. This research was made possible with the support of the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
JooHyeon Heo
Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology(UNIST)
Office: +82-52-217-1223
Copyright © Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology(UNIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Chemistry
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








