Home > Press > More than glitter: Scientists explain how gold nanoparticles easily penetrate cells, making them useful for delivering drugs
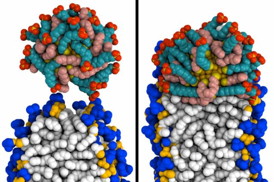 |
| MIT engineers created simulations of how a gold nanoparticle coated with special molecules can penetrate a membrane. At left, the particle (top) makes contact with the membrane. At right, it has fused to the membrane.
Image: Reid Van Lehn |
Abstract:
A special class of tiny gold particles can easily slip through cell membranes, making them good candidates to deliver drugs directly to target cells.
A new study from MIT materials scientists reveals that a special class of tiny gold particles can easily slip through cell membranes, making them good candidates to deliver drugs directly to target cells.
Video: Melanie Gonick/MIT
More than glitter: Scientists explain how gold nanoparticles easily penetrate cells, making them useful for delivering drugs
Cambridge, MA | Posted on July 21st, 2014A new study from MIT materials scientists reveals that these nanoparticles enter cells by taking advantage of a route normally used in vesicle-vesicle fusion, a crucial process that allows signal transmission between neurons. In the July 21 issue of Nature Communications, the researchers describe in detail the mechanism by which these nanoparticles are able to fuse with a membrane.
The findings suggest possible strategies for designing nanoparticles — made from gold or other materials — that could get into cells even more easily.
"We've identified a type of mechanism that might be more prevalent than is currently known," says Reid Van Lehn, an MIT graduate student in materials science and engineering and one of the paper's lead authors. "By identifying this pathway for the first time it also suggests not only how to engineer this particular class of nanoparticles, but that this pathway might be active in other systems as well."
The paper's other lead author is Maria Ricci of École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland. The research team, led by Alfredo Alexander-Katz, an associate professor of materials science and engineering, and Francesco Stellacci from EPFL, also included scientists from the Carlos Besta Institute of Neurology in Italy and Durham University in the United Kingdom.
Most nanoparticles enter cells through endocytosis, a process that traps the particles in intracellular compartments, which can damage the cell membrane and cause cell contents to leak out. However, in 2008, Stellacci, who was then at MIT, and Darrell Irvine, a professor of materials science and engineering and of biological engineering, found that a special class of gold nanoparticles coated with a mix of molecules could enter cells without any disruption.
"Why this was happening, or how this was happening, was a complete mystery," Van Lehn says.
Last year, Alexander-Katz, Van Lehn, Stellacci, and others discovered that the particles were somehow fusing with cell membranes and being absorbed into the cells. In their new study, they created detailed atomistic simulations to model how this happens, and performed experiments that confirmed the model's predictions.
Stealth entry
Gold nanoparticles used for drug delivery are usually coated with a thin layer of molecules that help tune their chemical properties. Some of these molecules, or ligands, are negatively charged and hydrophilic, while the rest are hydrophobic. The researchers found that the particles' ability to enter cells depends on interactions between hydrophobic ligands and lipids found in the cell membrane.
Cell membranes consist of a double layer of phospholipid molecules, which have hydrophobic lipid tails and hydrophilic heads. The lipid tails face in toward each other, while the hydrophilic heads face out.
In their computer simulations, the researchers first created what they call a "perfect bilayer," in which all of the lipid tails stay in place within the membrane. Under these conditions, the researchers found that the gold nanoparticles could not fuse with the cell membrane.
However, if the model membrane includes a "defect" — an opening through which lipid tails can slip out — nanoparticles begin to enter the membrane. When these lipid protrusions occur, the lipids and particles cling to each other because they are both hydrophobic, and the particles are engulfed by the membrane without damaging it.
In real cell membranes, these protrusions occur randomly, especially near sites where proteins are embedded in the membrane. They also occur more often in curved sections of membrane, because it's harder for the hydrophilic heads to fully cover a curved area than a flat one, leaving gaps for the lipid tails to protrude.
"It's a packing problem," Alexander-Katz says. "There's open space where tails can come out, and there will be water contact. It just makes it 100 times more probable to have one of these protrusions come out in highly curved regions of the membrane."
Mimicking nature
This phenomenon appears to mimic a process that occurs naturally in cells — the fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane. Vesicles are small spheres of membrane-like material that carry cargo such as neurotransmitters or hormones.
The similarity between absorption of vesicles and nanoparticle entry suggests that cells where a lot of vesicle fusion naturally occurs could be good targets for drug delivery by gold nanoparticles. The researchers plan to further analyze how the composition of the membranes and the proteins embedded in them influence the absorption process in different cell types. "We want to really understand all the constraints and determine how we can best design nanoparticles to target particular cell types, or regions of a cell," Van Lehn says.
"One could use the results from this paper to think about how to leverage these findings into improved nanoparticle delivery vehicles — for instance, perhaps new surface ligands for nanoparticles could be engineered to have improved affinity for both surface groups and lipid tails," says Catherine Murphy, a professor of chemistry at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign who was not involved in the study.
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation and the Swiss National Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah McDonnell
617-253-8923
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








