Home > Press > University of Illinois researchers demonstrate novel, tunable nanoantennas
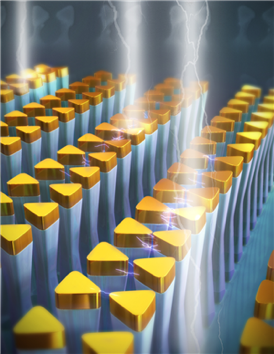 |
| Illustration of the pillar-based Au bowtie nanoantenna arrays undergoing selective actuation due to an electromagnetic-induced force. |
Abstract:
An interdisciplinary research team at the University of Illinois has developed a novel, tunable nanoantenna that paves the way for new kinds of plasmonic-based optomechanical systems whereby plasmonic field enhancement can actuate mechanical motion.
University of Illinois researchers demonstrate novel, tunable nanoantennas
Urbana, IL | Posted on July 14th, 2014"Recently, there has been a lot of interest in fabricating metal-based nanotextured surfaces that are pre-programmed to alter the properties of light in a specific way after incoming light interacts with it," explained Kimani Toussaint, an associate professor of mechanical science and engineering who led the research. "For our approach, one can take a nanoarray structure that was already fabricated and further reconfigure the plasmonic, and hence, optical properties of select antennas. Therefore, one can decide after fabrication, rather than before, how they want their nanostructure to modify light."
The researchers developed a novel, metal, pillar-bowtie nanoantenna (p-BNA) array template on 500-nanometer tall glass pillars (or posts). In doing so, they demonstrated that the gap size for either individual or multiple p-BNAs can be tuned down to approximately 5 nm (approx. 4x smaller than what is currently achievable using conventional electron-beam lithography techniques).
"On a fundamental level, our work demonstrates electron-beam based manipulation of nanoparticles an order of magnitude larger than previously possible, using a simple SEM operating at only a fraction of the electron energies of previous work," said Brian Roxworthy, who earned his PhD in electrical and computer engineering (ECE) at Illinois and was first author of the paper published in Nature Communications. ""The dramatic deformation of the nanoantennas we observe is facilitated by strong in-gap plasmonic modes excited by the passing electrons, which give rise to nanoNewton-magnitude gradient forces on the constituent metal particles."
The interdisiciplinary research team--that included Abdul Bhuiya (MS student in ECE student), Xin Yu (ECE post-grad), and K.C. Chow (a research engineer at the Micro and Nanotechnology Laboratory)—also demonstrated that a standard scanning electron microscope (SEM) can be used to deform either individual p-BNA structures or groups of p-BNAs within a sub-array with velocities as large as 60 nanometers per second. A photonic-crystal fiber was used to generate (quasi-white light) supercontinuum to probe the spectral response of select regions within the array.
The researchers said the importance of this work is three-fold: It enables tuning of the optical (plasmonic) response of the nanoantennas, down to the level of a single nanoantenna (approximately 250 nanometers across); it could lead to unique, spatially addressable nanophotonic devices for sensing and particle manipulation, for example; and, it provides a fertile platform for studying mechanical, electromagnetic, and thermal phenomena in a nanoscale system.
The team believes that the relatively high aspect ratio (pillar height-to-thickness) of 4.2 for the p-BNAs, along with a significant thermal contribution, permit sufficient compliance of the pillars to be actuated by electron-beam-induced gradient forces.
"Our fabrication process shows for the first time an innovative way of fabricating plasmonic nanoantenna structures under the SEM, which avoids complications such as proximity effects from conventional lithography techniques," Bhuiya said. "This process also reduces the gap of the nanoantennas down to ~5 nm under SEM with a controlled reduction rate. With this new fabrication technique, it opens an avenue to study different phenomena which leads to new exciting research fields."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kimani Toussaint
217-244-4088
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








