Home > Press > University of Illinois study advances limits for ultrafast nano-devices
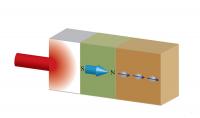 |
| Ultrafast laser light creates heat transport through the nonmagnetic/ferromagnetic/nonmagnetic tri-layer. The thermal excitation in the ferromagnetic layer produces spin current in the adjacent nonmagnetic layer in a picosecond timescale.
Credit: Gyung-Min Choi |
Abstract:
A recent study by researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign provides new insights on the physical mechanisms governing the interplay of spin and heat at the nanoscale, and addresses the fundamental limits of ultrafast spintronic devices for data storage and information processing.
University of Illinois study advances limits for ultrafast nano-devices
Urbana, IL | Posted on July 10th, 2014"Electrons carry a charge as well as spin-angular momentum. In a typical charge current, electrons' spin-angular-momentum is random so there is no spin current," explained David Cahill, a professor of materials science and engineering at Illinois. "However when electrons move with a partial alignment of spin-angular-momentum, we call it spin current which is the key element for nanoscale spintronic devices.
"It is understood that spin current can rotate magnetization. In other words, we can use spin current to select "0" or "1" state of magnetic memory devices. For ultrafast operation of such nano-devices, generation of spin current in picoseconds—one trillionth of a second—a time-scale that is difficult to achieve using electrical circuits, is highly desired," Cahill added.
"In a typical electrical circuit approach, spin current is driven by voltage difference across the structure. In this work, we utilized differences in temperature to generate spin currents," explained Gyung-Min Choi, lead author of the paper, "Spin current generated by thermally-driven ultrafast demagnetization," published in Nature Communications.
"A metallic ferromagnet has three energy reservoirs: electrons, magnons, and phonons," Choi stated. "Using ultra-short laser light, we created temperature differences between these reservoirs of thermal energy for a few picoseconds. The temperature difference between electron and magnon drives an exchange of spin-angular-momentum.
"Thus, we transport spin-angular-momentum from magnons to electrons, and this transport leads to ultrafast spin current," Choi added. "We refer to this spin current as thermally-driven and believe that our results extend the emerging discipline of spin caloritronics into the regime of picosecond time scales.
The benefits of thermal generation over electric generation are two-fold, according to Choi.
"Thermal spin generation has a potential for higher efficiency than spin generation by electrical currents. Our work shows that thermal spin current can be large enough to rotate magnetization. Although the amount of spin current is still smaller than what would be required for practical applications, we show the potential of thermal generation.
"The second advantage is the fast timescale. The time scale of spin currents generated by electrical currents is limited to a few nanoseconds. In this work, we are able to create spin current with timescale of a few picoseconds. Picosecond generation of spin current is desirable for fast operation of magnetic memory devices."
###
Supported by grants from the Army Research Office and the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Basic Energy Sciences, this work was carried out in the Laser and Spectroscopy Laboratory of the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory at Illinois.
In addition to Choi and Cahill, co-authors of the paper include, Byoung-Chul Min, Center for Spintronics Research, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul, and Kyung-Jin Lee, Department of Materials Science and Engineering and KU-KIST Graduate School of Converging Science and Technology, Korea University, Seoul.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David G. Cahill
217-333-6753
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








