Home > Press > Diamond plates create nanostructures through pressure, not chemistry: Method is more ecological than chemical processes
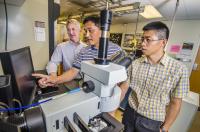 |
| Sandia National Laboratories researcher Hongyou Fan, center, points out a pressure result at the nanoscale to Sandia paper co-authors Paul Clem, left, and Binsong Li.
Credit: Photo by Randy Montoya, Sandia National Laboratories |
Abstract:
You wouldn't think that mechanical force — the simple kind used to eject unruly patrons from bars, shoe a horse or emboss the raised numerals on credit cards — could process nanoparticles more subtly than the most advanced chemistry.
Diamond plates create nanostructures through pressure, not chemistry: Method is more ecological than chemical processes
Albuquerque, NM | Posted on June 28th, 2014 Yet, in a current paper in Nature Communications, Sandia National Laboratories researcher Hongyou Fan and colleagues appear to have achieved a start toward that end.
Their newly patented and original method uses simple pressure — a kind of high-tech embossing — to produce finer and cleaner results in forming silver nanostructures than do chemical methods, which are not only inflexible in their results but leave harmful byproducts to dispose of.
Fan calls his approach "a simple stress-based fabrication method" that, when applied to nanoparticle arrays, forms new nanostructures with tunable properties.
"There is a great potential market for this technology," he said. "It can be readily and directly integrated into current industrial manufacturing lines without creating new expensive and specialized equipment."
Said Sandia co-author Paul Clem, "This is a foundational method that should enable a variety of devices, including flexible electronics such as antennas, chemical sensors and strain detectors." It also would produce transparent electrodes for solar cells and organic light-emitting diodes, Clem said.
The method was inspired by industrial embossing processes in which a patterned mask is applied with high external pressure to create patterns in the substrate, Fan said. "In our technology, two diamond anvils were used to sandwich nanoparticulate thin films. This external stress manually induced transitions in the film that synthesized new materials," he said.
The pressure, delivered by two diamond plates tightened by four screws to any controlled setting, shepherds silver nanospheres into any desired volume. Propinquity creates conditions that produce nanorods, nanowires and nanosheets at chosen thicknesses and lengths rather than the one-size-fits-all output of a chemical process, with no environmentally harmful residues.
While experiments reported in the paper were performed with silver — the most desirable metal because it is the most conductive, stable and optically interesting and becomes transparent at certain pressures — the method also has been shown to work with gold, platinum and other metallic nanoparticles
Clem said the researchers are now starting to work with semiconductors.
Bill Hammetter, manager of Sandia's Advanced Materials Laboratory, said, "Hongyou has discovered a way to build one structure into another structure — a capability we don't have now at the nanolevel. Eight or nine gigapascal —the amount of pressure at which phase change and new materials occur — are not difficult to reach. Any industry that has embossing equipment could lay a film of silver on a piece of paper, build a conductive pattern, then remove the extraneous material and be left with the pattern. A coating of nanoparticles that can build into another structure has a certain functionality we don't have right now. It's a discovery that hasn't been commercialized, but could be done today with the same equipment used by anyone who makes credit cards."
The method can be used to configure new types of materials. For example, under pressure, the dimensions of ordered three-dimensional nanoparticle arrays shrink. By fabricating a structure in which the sandwiching walls permanently provide that pressure, the nanoparticle array will remain at a constant state, able to transmit light and electricity with specific characteristics. This pressure-regulated fine-tuning of particle separation enables controlled investigation of distance-dependent optical and electrical phenomena.
At even higher pressures, nanoparticles are forced to sinter, or bond, forming new classes of chemically and mechanically stable nanostructures that no longer need restraining surfaces. These cannot be manufactured using current chemical methods.
Depending on the size, composition and phase orientation of the initial nanoparticle arrays, a variety of nanostructures or nanocomposites and 3-D interconnected networks are achievable.
The stress-induced synthesis processes are simple and clean. No thermal processing or further purification is needed to remove reaction byproducts.
###
This work was funded by the Department of Energy's Office of Science. Other authors of the paper are from Cornell University and Los Alamos National Laboratory.
####
About DOE/Sandia National Laboratories
Sandia National Laboratories is a multi-program laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Lockheed Martin Corp., for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration. With main facilities in Albuquerque, N.M., and Livermore, Calif., Sandia has major R&D responsibilities in national security, energy and environmental technologies and economic competitiveness.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
neal singer
505-845-7078
Copyright © DOE/Sandia National Laboratories
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








