Home > Press > Not all diamonds are forever: Rice University researchers see nanodiamonds created in coal fade away in seconds
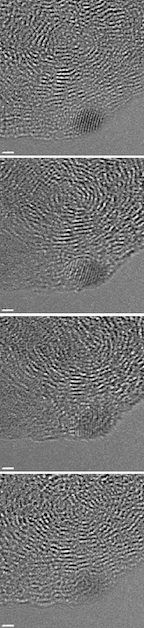 |
| A series of images shows a small nanodiamond (the dark spot in the lower right corner) reverting to anthracite. Rice University scientists saw nanodiamonds form in hydrogenated coal when hit by the electron beam used in high-resolution transmission electron microscopes. But smaller diamonds like this one degraded with subsequent images. The scale bar is 1 nanometer. Credit: Billups Lab/Rice University |
Abstract:
Images taken by Rice University scientists show that some diamonds are not forever.
The Rice researchers behind a new study that explains the creation of nanodiamonds in treated coal also show that some microscopic diamonds only last seconds before fading back into less-structured forms of carbon under the impact of an electron beam.
Not all diamonds are forever: Rice University researchers see nanodiamonds created in coal fade away in seconds
Houston, TX | Posted on May 22nd, 2014The research by Rice chemist Ed Billups and his colleagues appears in the American Chemical Society's Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
Billups and Yanqiu Sun, a former postdoctoral researcher in his lab, witnessed the interesting effect while working on ways to chemically reduce carbon from anthracite coal and make it soluble. First they noticed nanodiamonds forming amid the amorphous, hydrogen-infused layers of graphite.
It happened, they discovered, when they took close-ups of the coal with an electron microscope, which fires an electron beam at the point of interest. Unexpectedly, the energy input congealed clusters of hydrogenated carbon atoms, some of which took on the lattice-like structure of nanodiamonds.
"The beam is very powerful," Billups said. "To knock hydrogen atoms off of something takes a tremendous amount of energy."
Even without the kind of pressure needed to make macroscale diamonds, the energy knocked loose hydrogen atoms to prompt a chain reaction between layers of graphite in the coal that resulted in diamonds between 2 and 10 nanometers wide.
But the most "nano" of the nanodiamonds were seen to fade away under the power of the electron beam in a succession of images taken over 30 seconds.
"The small diamonds are not stable and they revert to the starting material, the anthracite," Billups said.
Billups turned to Rice theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson and his colleagues at the Technological Institute for Superhard and Novel Carbon Materials in Moscow to explain what the chemists saw. Yakobson, Pavel Sorokin and Alexander Kvashnin had already come up with a chart — called a phase diagram — that demonstrated how thin diamond films might be made without massive pressure.
They used similar calculations to show how nanodiamonds could form in treated anthracite and subbituminous coal. In this case, the electron microscope's beam knocks hydrogen atoms loose from carbon layers. Then the dangling bonds compensate by connecting to an adjacent carbon layer, which is prompted to connect to the next layer. The reaction zips the atoms into a matrix characteristic of diamond until pressure forces the process to halt.
Natural, macroscale diamonds require extreme pressures and temperatures to form, but the phase diagram should be reconsidered for nanodiamonds, the researchers said.
"There is a window of stability for diamonds within the range of 19-52 angstroms (tenths of a nanometer), beyond which graphite is more stable," Billups said. Stable nanodiamonds up to 20 nanometers in size can be formed in hydrogenated anthracite, they found, though the smallest nanodiamonds were unstable under continued electron-beam radiation.
Billups noted subsequent electron-beam experiments with pristine anthracite formed no diamonds, while tests with less-robust infusions of hydrogen led to regions with "onion-like fringes" of graphitic carbon, but no fully formed diamonds. Both experiments lent support to the need for sufficient hydrogen to form nanodiamonds.
Kvashnin is a former visiting student at Rice and a graduate student at the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT). Sorokin holds appointments at MIPT and the National University of Science and Technology, Moscow. Yakobson is Rice's Karl F. Hasselmann Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science, a professor of chemistry and a member of the Richard E. Smalley Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology. Billups is a professor of chemistry at Rice.
The Robert A. Welch Foundation, the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation and the Russian Foundation for Basic Research supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,920 undergraduates and 2,567 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6.3-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for “best value” among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








