Home > Press > New lithium battery created in Japan: Using a parasitic conduction mechanism, technology described in the journal 'APL Materials' promises safer batteries in the future
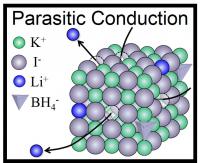 |
| This image shows synthesis of cubic LiBH4 at ambient pressure and Parasitic Conduction Mechanism exhibited in KI - LiBH4 solid solution.
Credit: Hitoshi Takamura/Tohoku Univ. |
Abstract:
The long life of lithium ion batteries makes them the rechargeable of choice for everything from implantable medical devices to wearable consumer electronics. But lithium ion batteries rely on liquid chemistries involving lithium salts dissolved in organic solvents, creating flame risks that would be avoided if the cells were completely solid-state.
New lithium battery created in Japan: Using a parasitic conduction mechanism, technology described in the journal 'APL Materials' promises safer batteries in the future
Washington, DC | Posted on May 20th, 2014Now a team of researchers at Tohoku University in Japan has created a new type of lithium ion conductor for future batteries that could be the basis for a whole new generation of solid-state batteries. It uses rock salt Lithium Borohydride (LiBH4), a well-known agent in organic chemistry laboratories that has been considered for batteries before, but up to now has only worked at high temperatures or pressures.
In the journal APL Materials, from AIP Publishing, the researchers describe how they doped a cubic lattice of KI molecules with the LiBH4. This allowed them to stabilize the high-pressure form of Lithium borohydride and make a solid solution at normal atmospheric pressure that was stable at room temperature.
In making the new technology, the team made the peculiar discovery that the Li+ ions functioned like pure Li+ ion conductors, even though they were just doping the KI lattices. This is the reverse of the normal doping technique, in which a small amount of stabilizing element would be added to an ionic conductor abundant in Lithium.
"In other words, LiBH4 is a sort of 'parasite' but not a host material," said Hitoshi Takamura who led the research at Tohoku University. He and his colleagues have called this mechanism "parasitic conduction" and have suggested that it could be broadly applied in the search for new batteries -- anywhere that small amounts of Li+ ions could be used to dope an oxide, sulfide, halide or nitride host material.
"This work suggests the potential of this mechanism in the ongoing search for the perfect material for use in solid state batteries," added Takamura. "The urgency of this quest has been abundantly clear after the grounding of so many aircraft in recent months."
####
About American Institute of Physics
APL Materials is a new open access journal featuring original research on significant topical issues within the field of materials science. See: aplmaterials.aip.org
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Alliances/Trade associations/Partnerships/Distributorships
![]() Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








