Home > Press > High-Performance, Low-Cost Ultracapacitors Built with Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes: Future devices based on technology could bridge gap between batteries and conventional capacitors in portable electronics and hybrid electric vehicles
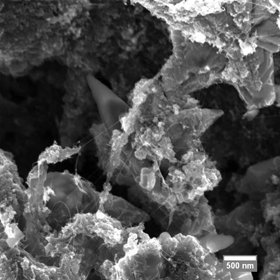 |
| A scanning electron microscope image shows the ultracapacitor’s composite film containing graphene flakes and single-walled carbon nanotubes. Credit: Journal of Applied Physics |
Abstract:
By combining the powers of two single-atom-thick carbon structures, researchers at the George Washington University's Micro-propulsion and Nanotechnology Laboratory have created a new ultracapacitor that is both high performance and low cost.
High-Performance, Low-Cost Ultracapacitors Built with Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes: Future devices based on technology could bridge gap between batteries and conventional capacitors in portable electronics and hybrid electric vehicles
Melville, NY | Posted on April 23rd, 2014
High-Performance, Low-Cost Ultracapacitors Built with Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes
Future devices based on technology could bridge gap between batteries and conventional capacitors in portable electronics and hybrid electric vehicles
From the Journal:
Journal of Applied Physics
For immediate release
By Jason Bardi
WASHINGTON D.C., April 22, 2014 -- By combining the powers of two single-atom-thick carbon structures, researchers at the George Washington University's Micro-propulsion and Nanotechnology Laboratory have created a new ultracapacitor that is both high performance and low cost.
The device, described in the Journal of Applied Physics, capitalizes on the synergy brought by mixing graphene flakes with single-walled carbon nanotubes, two carbon nanostructures with complementary properties.
Ultracapacitors are souped-up energy storage devices that hold high amounts of energy and can also quickly release that energy in a surge of power. By combining the high energy-density properties of batteries with the high power-density properties of conventional capacitors, ultracapacitors can boost the performance of electric vehicles, handheld electronics, audio systems and more.
Single-walled carbon nanotubes and graphene both have unique and excellent electronic, thermal, and mechanical properties that make them attractive materials for designing new ultracapacitors, said Jian Li, first author on the paper. Many groups had explored the use of the two materials separately, but few had looked at combining them, he said.
"In our lab we developed an approach by which we can obtain both single-walled carbon nanotubes and graphene, so we came up with the idea to take advantage of the two promising carbon nanomaterials together," added Michael Keidar, a professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering in the School of Engineering and Applied Science at GW, and director of the Micro-propulsion and Nanotechnology Laboratory.
The researchers synthesized the graphene flakes and nanotubes by vaporizing a hollow graphite rod filled with metallic catalyst powder with an electric arc. They then mixed the two nanostructures together to form an ink that they rolled onto paper, a common separator for current commercial capacitors.
The combination device's specific capacitance, a measurement of the performance of a capacitor per unit of weight, was three times higher than the specific capacitance of a device made from carbon nanotubes alone.
The advantage of the hybrid structure, Li explained, is that the graphene flakes provide high surface area and good in-plane conductivity, while the carbon nanotubes connect all of the structures to form a uniform network.
While other types of ultracapacitors have also achieved the high specific capacitance of the graphene/nanotube hybrid, the researchers say, the main advantage of the combination approach is its low costs, since the team has developed a simple way to manufacture large amounts of the desirable mix of carbon nanostructures.
The hybrid ultracapacitor is also small and light, an advantage as electronic devices get ever smaller.
MORE INFORMATION: The George Washington University's Micro-propulsion and Nanotechnology Laboratory: https://www.mpnl.seas.gwu.edu
This work was supported by the NSF/DOE Partnership in Plasma Science and Technology (NSF Grant No. CBET-0853777 and DOE Grant No. DE-SC0001169), and an NSF Award (Title: EAGER: Exploring plasma mechanism of synthesis of graphene in arc discharge, NSF Award No. 1249213).
####
About American Institute of Physics
Journal of Applied Physics
Journal of Applied Physics is an influential international journal publishing significant new experimental and theoretical results of applied physics research.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








