Home > Press > Researchers improve performance of III-V nanowire solar cells on graphene: Imagine a field of small wires—standing at attention like a tiny field of wheat—gathering the Sun’s rays as the first step in solar energy conversion
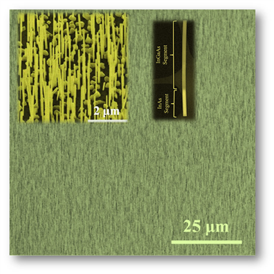 |
| A dense array of nanowires grown directly on graphene. The insets show a higher magnification SEM view of the array and a STEM image of a single, axially heterostructured InGaAs/InAs nanowire. |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have achieved new levels of performance for seed-free and substrate-free arrays of nanowires from class of materials called III-V (three-five) directly on graphene. These compound semiconductors hold particular promise for applications involving light, such as solar cells or lasers.
Researchers improve performance of III-V nanowire solar cells on graphene: Imagine a field of small wires—standing at attention like a tiny field of wheat—gathering the Sun’s rays as the first step in solar energy conversion
Urbana, IL | Posted on March 24th, 2014"Over the past two decades, research in the field of semiconductor nanowires has helped to reshape our understanding of atomic-scale crystal assembly and uncover novel physical phenomena at the nanometer scale," explained Xiuling Li, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at Illinois. In the March 20th issue of Advanced Materials, the researchers present the first report of a novel solar cell architecture based on dense arrays of coaxial p-n junction InGaAs nanowires on InAs stems grown directly on graphene without any metal catalysts or lithographic patterning.
"In this work, we have overcome the surprising structure (phase segregation) and successfully grown single phase InGaAs and demonstrated very promising solar cell performance," explained postdoctoral researcher Parsian Mohseni, first author of the study.
"Depending on the materials, nanowires can be used for functional electronics and optoelectronics applications," Mohseni added. "The main benefits of this III-V photovoltaic solar cell design are that it is fairly low-cost, substrate-free, and has a built-in back side contact, while being conducive to integration within other flexible device platforms."
Li's research group uses a method called van der Waals epitaxy to grow nanowires from the bottom up on a two-dimensional sheet, in this case, graphene. Gases containing gallium, indium, and arsenic are pumped into a chamber where the graphene sheet sits, prompting the nanowires self-assemble, growing by themselves into a dense carpet of vertical wires across the graphene's surface.
In their earlier work (Nano Letters 2013) using a graphene sheet, the researchers discovered that InGaAs wires grown on graphene spontaneously segregate into an indium arsenide (InAs) core with an InGaAs shell around the outside of the wire. To improve the materials' efficiencies for solar power conversion, the researchers bypassed the unique van der Waals epitaxy induced spontaneous phase segregation by inserting InAs segments in between. The resulted ternary InGaAs NW arrays are vertical, non-tapered, controllable in size, height, and doping, and broadly tunable in composition thus energy for monolithic heterogeneous integration with 2D van der Waals sheets including graphene.
Under air mass 1.5 global solar illumination, the core-shell In0.25Ga0.75As (Eg ~ 1.1 eV) nanowire arrays on graphene demonstrate a conversion efficiency of 2.51 %, representing a new record for substrate-free, III-V NW-based solar cells.
"Although InGaAs is far from being the optimum bandgap materials for high efficiency solar cells, the direct epitaxy on graphene platform established here has significant implications for a wide variety of III-V compound semiconductor NW based solar cells on graphene, as well as light emitters and multi-junction tandem solar cells, all of which can be released for flexible applications," Li said.
In addition to Li and Mohseni, postdoctoral researcher Ashkan Behnam, and graduate students Joshua Wood, Xiang Zhao, Ning C. Wang, and Ki Jun Yu, were co-authors of the paper along with professors Angus Rockett and John A. Rogers (materials science), Joseph W. Lyding (electrical and computer engineering), and Eric Pop at Stanford University. Li also is affiliated with the Micro and Nanotechnology Laboratory, the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory, and the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at Illinois.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Xiuling Li
217-265-6354
Writer:
Rick Kubetz
Engineering Communications Office
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
217/244-7716
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








