Home > Press > How to create selective holes in graphene: New technique developed at MIT produces highly selective filter materials, could lead to more efficient desalination
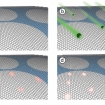 |
| The MIT researchers used a four-step process to create filters from graphene (shown here): (a) a one-atom-thick sheet of graphene is placed on a supporting structure; (b) the graphene is bombarded with gallium ions; (c) wherever the gallium ions strike the graphene, they create defects in its structure; and (d) when etched with an oxidizing solution, each of those defects grows into a hole in the graphene sheet. The longer the material stays in the oxidizing bath, the larger the holes get. Image courtesy of the researchers |
Abstract:
Researchers have devised a way of making tiny holes of controllable size in sheets of graphene, a development that could lead to ultrathin filters for improved desalination or water purification.
How to create selective holes in graphene: New technique developed at MIT produces highly selective filter materials, could lead to more efficient desalination
Cambridge, MA | Posted on February 25th, 2014The team of researchers at MIT, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and in Saudi Arabia succeeded in creating subnanoscale pores in a sheet of the one-atom-thick material, which is one of the strongest materials known. Their findings are published in the journal Nano Letters.
The concept of using graphene, perforated by nanoscale pores, as a filter in desalination has been proposed and analyzed by other MIT researchers. The new work, led by graduate student Sean O'Hern and associate professor of mechanical engineering Rohit Karnik, is the first step toward actual production of such a graphene filter.
Making these minuscule holes in graphene — a hexagonal array of carbon atoms, like atomic-scale chicken wire — occurs in a two-stage process. First, the graphene is bombarded with gallium ions, which disrupt the carbon bonds. Then, the graphene is etched with an oxidizing solution that reacts strongly with the disrupted bonds — producing a hole at each spot where the gallium ions struck. By controlling how long the graphene sheet is left in the oxidizing solution, the MIT researchers can control the average size of the pores.
A big limitation in existing nanofiltration and reverse-osmosis desalination plants, which use filters to separate salt from seawater, is their low permeability: Water flows very slowly through them. The graphene filters, being much thinner, yet very strong, can sustain a much higher flow. "We've developed the first membrane that consists of a high density of subnanometer-scale pores in an atomically thin, single sheet of graphene," O'Hern says.
For efficient desalination, a membrane must demonstrate "a high rejection rate of salt, yet a high flow rate of water," he adds. One way of doing that is decreasing the membrane's thickness, but this quickly renders conventional polymer-based membranes too weak to sustain the water pressure, or too ineffective at rejecting salt, he explains.
With graphene membranes, it becomes simply a matter of controlling the size of the pores, making them "larger than water molecules, but smaller than everything else," O'Hern says — whether salt, impurities, or particular kinds of biochemical molecules.
The permeability of such graphene filters, according to computer simulations, could be 50 times greater than that of conventional membranes, as demonstrated earlier by a team of MIT researchers led by graduate student David Cohen-Tanugi of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. But producing such filters with controlled pore sizes has remained a challenge. The new work, O'Hern says, demonstrates a method for actually producing such material with dense concentrations of nanometer-scale holes over large areas.
"We bombard the graphene with gallium ions at high energy," O'Hern says. "That creates defects in the graphene structure, and these defects are more chemically reactive." When the material is bathed in a reactive oxidant solution, the oxidant "preferentially attacks the defects," and etches away many holes of roughly similar size. O'Hern and his co-authors were able to produce a membrane with 5 trillion pores per square centimeter, well suited to use for filtration. "To better understand how small and dense these graphene pores are, if our graphene membrane were to be magnified about a million times, the pores would be less than 1 millimeter in size, spaced about 4 millimeters apart, and span over 38 square miles, an area roughly half the size of Boston," O'Hern says.
With this technique, the researchers were able to control the filtration properties of a single, centimeter-sized sheet of graphene: Without etching, no salt flowed through the defects formed by gallium ions. With just a little etching, the membranes started allowing positive salt ions to flow through. With further etching, the membranes allowed both positive and negative salt ions to flow through, but blocked the flow of larger organic molecules. With even more etching, the pores were large enough to allow everything to go through.
Scaling up the process to produce useful sheets of the permeable graphene, while maintaining control over the pore sizes, will require further research, O'Hern says.
Karnik says that such membranes, depending on their pore size, could find various applications. Desalination and nanofiltration may be the most demanding, since the membranes required for these plants would be very large. But for other purposes, such as selective filtration of molecules — for example, removal of unreacted reagents from DNA — even the very small filters produced so far might be useful.
"For biofiltration, size or cost are not as critical," Karnik says. "For those applications, the current scale is suitable."
The work also included Jing Kong, the ITT Career Development Associate Professor of Electrical Engineering; MIT graduate students Michael Boutilier and Yi Song; researcher Juan-Carlos Idrobo of the Oak Ridge National Laboratory; and professors Tahar Laoui and Muataz Atieh of the King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM). The project received support from the Center for Clean Water and Clean Energy at MIT and KFUPM and the U.S. Department of Energy.
###
Written by David L. Chandler, MIT News Office
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Abby Abazorius
MIT News Office
617.253.2709
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








