Home > Press > Study shows how water dissolves stone, molecule by molecule: International team uses computers, experiments to better predict chemical dissolution
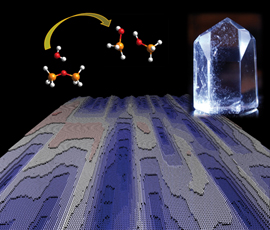 |
| The dissolution process of a crystalline structure in water is shown: two bonded SiO4 -- molecules dissolve (top left), a quartz crystal (top right) and the computer-simulated surface of a dissolving crystalline structure (below). CREDIT: MARUM & Rice University |
Abstract:
Scientists from Rice University and the University of Bremen's Center for Marine Environmental Sciences (MARUM) in Germany have combined cutting-edge experimental techniques and computer simulations to find a new way of predicting how water dissolves crystalline structures like those found in natural stone and cement.
Study shows how water dissolves stone, molecule by molecule: International team uses computers, experiments to better predict chemical dissolution
Houston, TX | Posted on December 5th, 2013In a new study featured on the cover of the Nov. 28 issue of the Journal of Physical Chemistry C, the team found their method was more efficient at predicting the dissolution rates of crystalline structures in water than previous methods. The research could have wide-ranging impacts in diverse areas, including water quality and planning, environmental sustainability, corrosion resistance and cement construction.
"We need to gain a better understanding of dissolution mechanisms to better predict the fate of certain materials, both in nature and in man-made systems," said lead investigator Andreas Lüttge, a professor of mineralogy at MARUM and professor emeritus and research professor in Earth science at Rice. His team specializes in studying the thin boundary layer that forms between minerals and fluids.
Boundary layers are ubiquitous in nature; they occur when raindrops fall on stone, water seeps through soil and the ocean meets the sea floor. Scientists and engineers have long been interested in accurately explaining how crystalline materials, including many minerals and stones, interact with and are dissolved by water. Calculations about the rate of these dissolution processes are critical in many fields of science and engineering.
In the new study, Lüttge and lead author Inna Kurganskaya, a research associate in Earth science at Rice, studied dissolution processes using quartz, one of the most common minerals found in nature. Quartz, or silicon dioxide, is a type of silicate, the most abundant group of minerals in Earth's crust.
At the boundary layer where quartz and water meet, multiple chemical reactions occur. Some of these happen simultaneously and others take place in succession. In the new study, the researchers sought to create a computerized model that could accurately simulate the complex chemistry at the boundary layer.
"The new model simulates the dissolution kinetics at the boundary layer with greater precision than earlier stochastic models operating at the same scale," Kurganskaya said. "Existing simulations rely on rate constants assigned to a wide range of possible reactions, and as a result, the total material flux from the surface have an inherent variance range -- a plus or minus factor that is always there."
One reason the team's simulations more accurately represent real processes is that its models incorporate actual measurements from cutting-edge instruments and from high-tech materials, including glass ceramics and nanomaterials. With a special imaging technique called "vertical scanning interferometry," which the group at MARUM and Rice helped to develop, the team scanned the crystal surfaces of both minerals and manufactured materials to generate topographic maps with a resolution of a just a few nanometers, or billionths of a meter.
"We found that dissolution rates that were predicted using rate constants were sometimes off by as much as two orders of magnitude," Lüttge said.
The new method for more precisely predicting dissolution processes could revolutionize the way engineers and scientists make many calculations related to a myriad of things, including the stability of building materials, the longevity of materials used for radioactive waste storage and more, he said.
"Further work is needed to prove the broad utility of the method," he said. "In the next phase of research, we plan to test our simulations on larger systems and over longer periods."
The research was supported by the Global Climate and Energy Project at Stanford University.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/AboutRiceU.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Jade Boyd
713-348-6778
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() A copy of the Journal of Physical Chemistry C paper is available at:
A copy of the Journal of Physical Chemistry C paper is available at:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








