Home > Press > Nanorobot for transporting drugs in the body: The first step has been taken towards developing a nanorobot that – in the long run – will enable the targeted transport of medications in the body
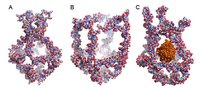 |
| Figuren viser et nano-bur, hvor otte unikke DNA-molekyler bliver blandet sammen. Nano-buret har fire funktionelle elementer, som forandrer sig ved ændringer i omgivelsernes temperatur. Disse forandringer enten lukker (1A) eller åbner (1B) nano-buret. Ved at udnytte temperaturforandringer i omgivelserne har forskerne dermed fanget et aktivt enzym kaldet horseradish peroxidase (HRP) inde i nano-buret (1C) Figur: Sissel Juul |
Abstract:
A nanorobot is a popular term for molecules with a unique property that enables them to be programmed to carry out a specific task. In collaboration with colleagues in Italy and the USA, researchers at Aarhus University have now taken a major step towards building the first nanorobot of DNA molecules that can encapsulate and release active biomolecules.
Nanorobot for transporting drugs in the body: The first step has been taken towards developing a nanorobot that – in the long run – will enable the targeted transport of medications in the body
Aarhus, Denmark | Posted on December 2nd, 2013In time, the nanorobot (also called a DNA nanocage) will no doubt be used to transport medications around in the body and thereby have a targeted effect on diseased cells.
Design using the body's natural molecules
Using DNA self-assembly, the researchers designed eight unique DNA molecules from the body's own natural molecules. When these molecules are mixed together, they spontaneously aggregate in a usable form - the nanocage (see figure).
The nanocage has four functional elements that transform themselves in response to changes in the surrounding temperature. These transformations either close (figure 1A) or open (figure 1B) the nanocage. By exploiting the temperature changes in the surroundings, the researchers trapped an active enzyme called horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in the nanocage (figure 1C). They used HRP as a model because its activity is easy to trace.
This is possible because the nanocage's outer lattice has apertures with a smaller diameter than the central spherical cavity. This structure makes it possible to encapsulate enzymes or other molecules that are larger than the apertures in the lattice, but smaller than the central cavity.
The researchers have just published these results in the renowned journal ACS Nano. Here the researchers show how they can utilise temperature changes to open the nanocage and allow HRP to be encapsulated before it closes again.
They also show that HRP retains its enzyme activity inside the nanocage and converts substrate molecules that are small enough to penetrate the nanocage to products inside.
The encapsulation of HRP in the nanocage is reversible, in such a way that the nanocage is capable of releasing the HRP once more in reaction to temperature changes. The researchers also show that the DNA nanocage - with its enzyme load - can be taken up by cells in culture.
Looking towards the future, the concept behind this nanocage is expected to be used for drug delivery, i.e. as a means of transport for medicine that can target diseased cells in the body in order to achieve a more rapid and more beneficial effect.
The research was carried out at the Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics and the Interdisciplinary Nanoscience Centre (iNANO), Aarhus University, in collaboration with researchers from Duke University (USA) and the University of Rome (Italy).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Birgitta R. Knudsen
(45) 60-20-26-73
Postdoctoral Fellow Sissel Juul
Department of Biomedical Engineering
Duke University
Durham, North Carolina, USA
mobile: +1 919 323 2291
Copyright © Aarhus University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Link to the scientific article in ACS Nano:
Link to the scientific article in ACS Nano:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








